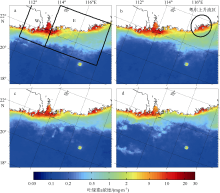
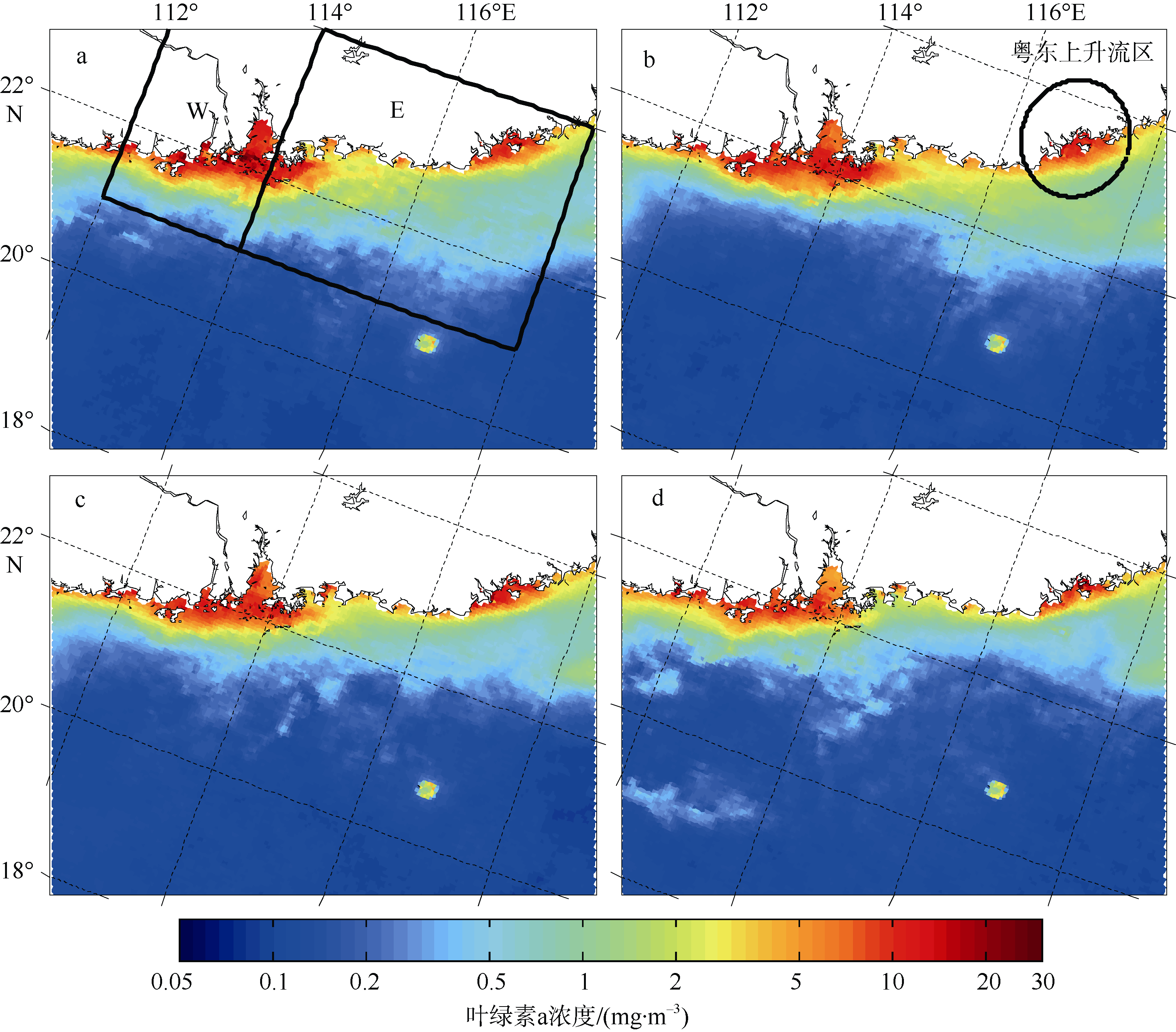
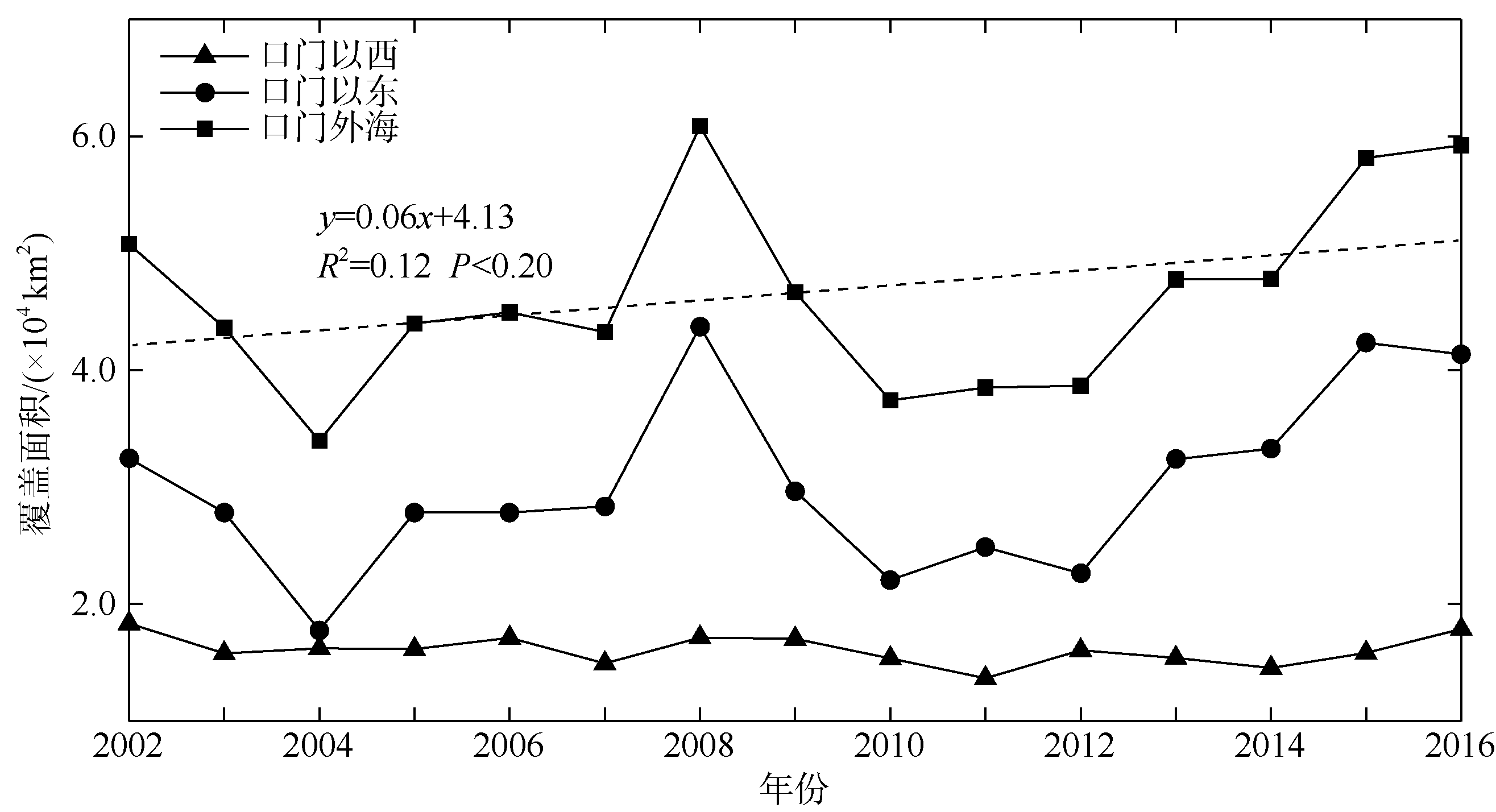
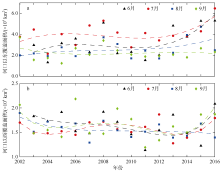
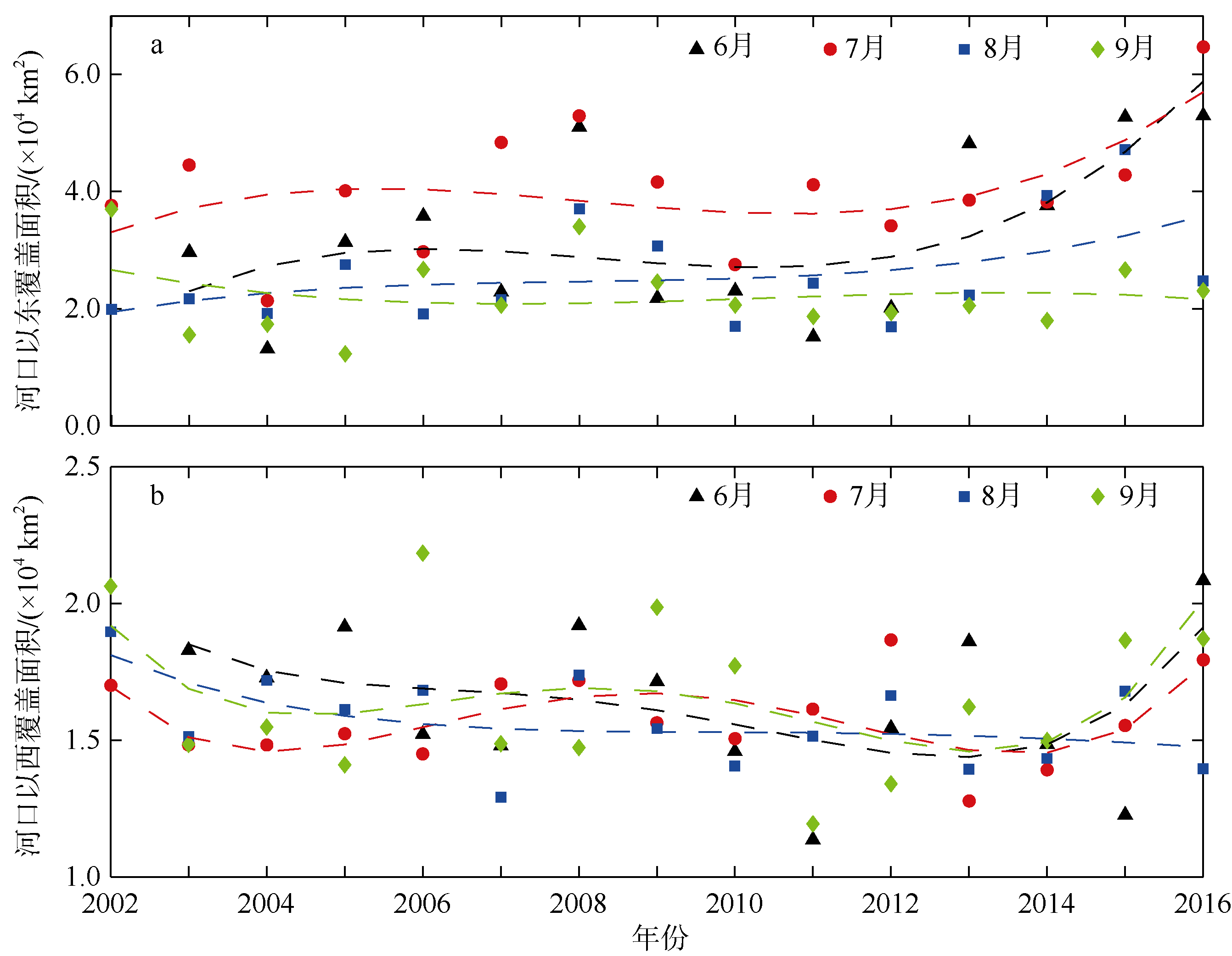
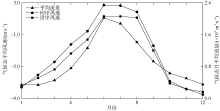
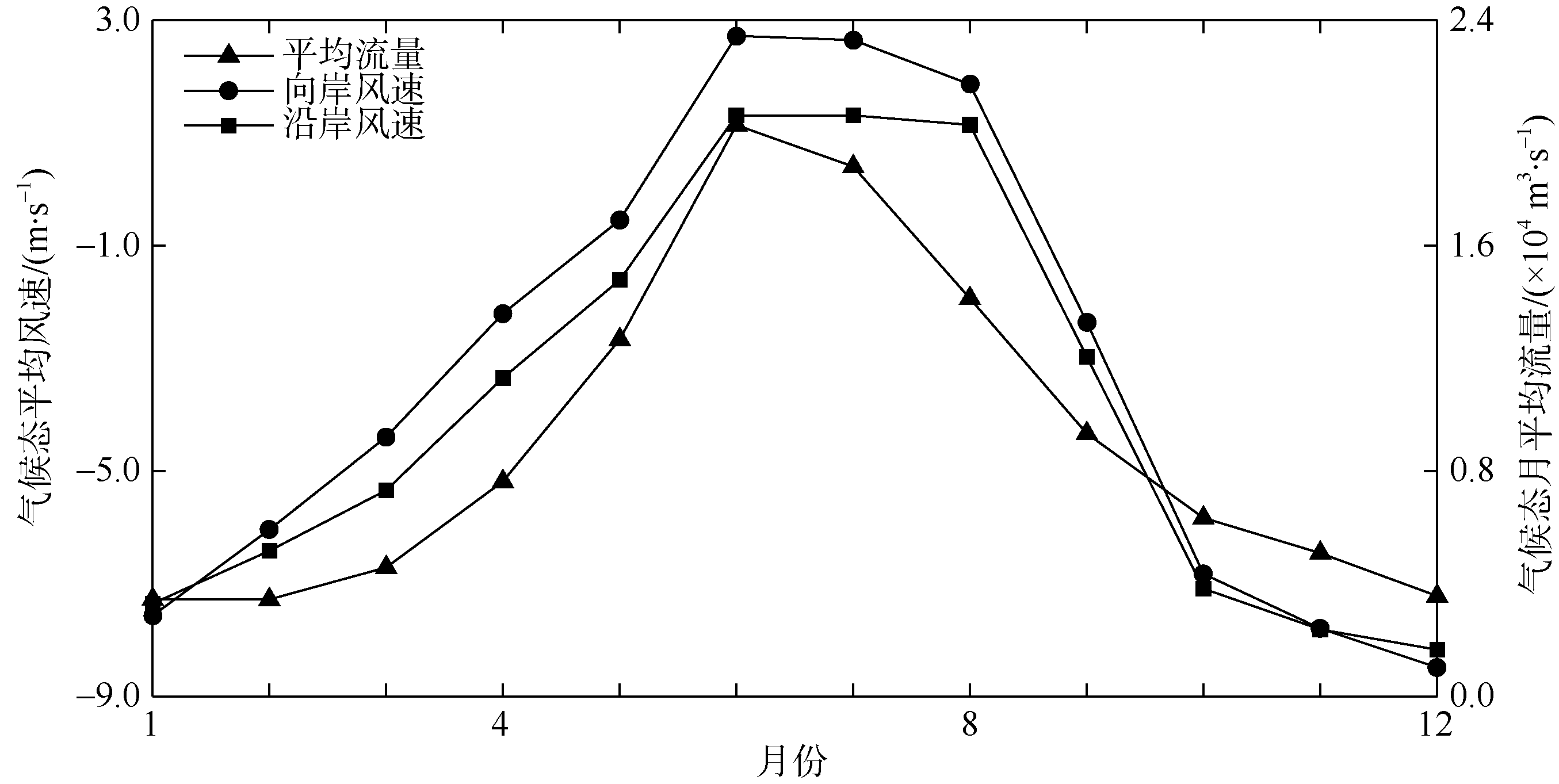
| 1 |
胡嘉镗 , 2009. 珠江三角洲河网与河口水-沙-污染物通量模拟研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学.
|
|
HU JIATANG , 2009. Modeling the mass fluxes of water, suspended sediment and pollutants for the river-network and estuary in the Pearl River Delta[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-Sen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 2 |
柯志新, 黄良民, 谭烨辉 , 等, 2013. 2008年夏末南海北部叶绿素a的空间分布特征及其影响因素[J]. 热带海洋学报, 32(4):51-57.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.008
|
|
KE ZHIXIN, HUANG LIANGMIN, TAN YEHUI , et al, 2013. Spatial distribution of chlorophyll a and its relationships with environmental factors in northern South China Sea in late summer 2008[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 32(4):51-57 (in Chinese with English abstract).
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-5470.2013.04.008
|
| 3 |
谢萍 , 2005. 珠江来水来沙特征及三角洲网河区水沙再次分配研究[D]. 广州: 中山大学.
|
|
XIE PING , 2005. Study on discharge and sediment characteristics of the Pearl River and changes of diversion ration of flow and sediment in the network area[D]. Guangzhou: Sun Yat-sen University (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 4 |
叶海军 , 2013. 台风对南海浮游植物分布及其粒径组成的影响[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学.
|
|
YE HAIJUN , 2013. Typhoon impact on marine phytoplankton distribution and its size classes in the South China Sea[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences (in Chinese with English abstract).
|
| 5 |
赵焕庭 , 1990. 珠江河口演变[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社.
|
|
ZHAO HUANTING , 1990. Evolution of Pearl River estuary[M]. Beijing: China Ocean Press (in Chinese).
|
| 6 |
BAI YAN, HE XIANGQIANG, PAN DELU , et al, 2014. Summertime Changjiang River plume variation during 1998-2010[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research Oceans, 119(9):6238-6257.
doi: 10.1002/2014JC009866
|
| 7 |
BAI YAN, HUANG T H, HE XIANQIANG , et al, 2015. Intrusion of the Pearl River plume into the main channel of the Taiwan Strait in summer[J]. Journal of Sea Research, 95:1-15.
doi: 10.1016/j.seares.2014.10.003
|
| 8 |
CAI WEIJUN, DAI MINHAN, WANG YONGCHEN , et al, 2004. The biogeochemistry of inorganic carbon and nutrients in the Pearl River estuary and the adjacent Northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(12):1301-1319.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.04.005
|
| 9 |
CHEN BINGZHANG, WANG LEI, SONG SHUQUN , et al, 2011. Comparisons of picophytoplankton abundance, size, and fluorescence between summer and winter in northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 31(14):1527-1540.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2011.06.018
|
| 10 |
DAI MINHAN, ZHAI WEIDONG, CAI WEIJUN , et al, 2008. Effects of an estuarine plume-associated bloom on the carbonate system in the lower reaches of the Pearl River estuary and the coastal zone of the northern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 28(12):1416-1423.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2007.04.018
|
| 11 |
DONG LIXIAN, SU JILAN, WONG L A , et al, 2004. Seasonal variation and dynamics of the Pearl River plume[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16):1761-1777.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.006
|
| 12 |
GAN JIANPING, LI LI, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2009. Interaction of a river plume with coastal upwelling in the northeastern South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 29(4):728-740.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2008.12.002
|
| 13 |
GAN JIANPING, LU ZHONGMING, DAI MINHAN , et al, 2010. Biological response to intensified upwelling and to a river plume in the northeastern South China Sea: A modeling study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 115(C9):C09001, doi: 10.1029/2009JC005569.
|
| 14 |
HE X Q, BAI Y, PAN D L , et al, 2013. Satellite views of the seasonal and interannual variability of phytoplankton blooms in the eastern China seas over the past 14yr (1998-2011)[J]. Biogeosciences, 10(7):4721-4739.
doi: 10.5194/bg-10-4721-2013
|
| 15 |
HO A Y T, XU JIE, YIN KEDONG , et al, 2010. Phytoplankton biomass and production in subtropical Hong Kong waters: influence of the Pearl River outflow[J]. Estuaries & Coasts, 33(1):170-181.
|
| 16 |
KIM H C, YAMAGUCHI H, YOO S , et al, 2009. Distribution of Changjiang Diluted Water detected by satellite chlorophyll-a and its interannual variation during 1998-2007[J]. Journal of Oceanography, 65(1):129-135.
doi: 10.1007/s10872-009-0013-0
|
| 17 |
LI Q P, ZHOU WEIWEN, CHEN YINCHAO , et al, 2018. Phytoplankton response to a plume front in the northern South China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 15(8):2551-2563.
doi: 10.5194/bg-15-2551-2018
|
| 18 |
LIU HUAXUE, SONG XINGYU, HUANG LIANGMIN , et al, 2011. Phytoplankton biomass and production in northern South China Sea during summer: Influenced by Pearl River discharge and coastal upwelling[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 31(3):133-136.
doi: 10.1016/j.chnaes.2011.02.001
|
| 19 |
LIU MEILING, LIU XIANGNAN, MA AOHUI , et al, 2014. Spatio-temporal stability and abnormality of chlorophyll-a in the Northern South China Sea during 2002-2012 from MODIS images using wavelet analysis[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 75:15-27.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.12.010
|
| 20 |
LU FENGHUI, NI HONGGANG, LIU FENG , et al, 2009. Occurrence of nutrients in riverine runoff of the Pearl River Delta, South China[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 376(1-2):107-115.
doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2009.07.018
|
| 21 |
LU ZHONGMING, GAN JIANPING , 2015. Controls of seasonal variability of phytoplankton blooms in the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 117:86-96.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsr2.2013.12.011
|
| 22 |
NING X, LIU Z, CAI Y , et al, 1998. Physicobiological oceanographic remote sensing of the East China Sea: Satellite and in situ observations[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 103(C10):21623-21635.
|
| 23 |
OU SUYING, ZHANG HONG, WANG DONGXIAO , 2009. Dynamics of the buoyant plume off the Pearl River Estuary in summer[J]. Environmental Fluid Mechanics, 9(5):471-492.
doi: 10.1007/s10652-009-9146-3
|
| 24 |
PAN GANG, CHAI FEI, TANG DANLING , et al, 2017. Marine phytoplankton biomass responses to typhoon events in the South China Sea based on physical-biogeochemical model[J]. Ecological Modelling, 356:38-47.
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolmodel.2017.04.013
|
| 25 |
SHANG S, DONG Q, LEE Z , et al, 2011. MODIS observed phytoplankton dynamics in the Taiwan Strait: an absorption-based analysis[J]. Biogeosciences, 8:841-850.
doi: 10.5194/bg-8-841-2011
|
| 26 |
SHANG S L, DONG Q, HU C M , et al, 2014. On the consistency of MODIS chlorophyll a products in the northern South China Sea[J]. Biogeosciences, 11(2):269-280.
doi: 10.5194/bg-11-269-2014
|
| 27 |
SHU YEQIANG, ZHU JIANG, WANG DONGXIAO , et al, 2009. Performance of four sea surface temperature assimilation schemes in the South China Sea[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 29(11-12):1489-1501.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2009.03.016
|
| 28 |
SHU YEQIANG, WANG DONGXIAO, ZHU JIANG , et al, 2011. The 4-D structure of upwelling and Pearl River plume in the northern South China Sea during summer 2008 revealed by a data assimilation model[J]. Ocean Modelling, 36(3-4):228-241.
doi: 10.1016/j.ocemod.2011.01.002
|
| 29 |
SU JILAN , 2004. Overview of the South China Sea circulation and its influence on the coastal physical oceanography outside the Pearl River Estuary[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16):1745-1760.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.005
|
| 30 |
YIN KEDONG, ZHANG JIANLIN, QIAN PEIYUAN , et al, 2004. Effect of wind events on phytoplankton blooms in the Pearl River estuary during summer[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 24(16):1909-1923.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2004.06.015
|
| 31 |
ZHANG XIA, SHI ZHEN, LIU QINGXIA , et al, 2013. Spatial and temporal variations of picoplankton in three contrasting periods in the Pearl River Estuary, South China[J]. Continental Shelf Research, 56:1-12.
doi: 10.1016/j.csr.2013.01.015
|
| 32 |
ZHANG YUANZHI, LIN HUI, CHEN CHUQUN , et al, 2011. Estimation of chlorophyll-a concentration in estuarine waters: case study of the Pearl River estuary, South China Sea[J]. Environmental Research Letters, 6(2):024016.
doi: 10.1088/1748-9326/6/2/024016
|
| 33 |
ZHAO HUI, TANG DANLING, WANG DONGXIAO , 2009. Phytoplankton blooms near the Pearl River Estuary induced by Typhoon Nuri[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Oceans, 114:C12027, doi: 10.1029/2009JC005384.
|
| 34 |
ZHAO W J, WANG G Q, CAO W X , et al, 2014. Assessment of SeaWiFS, MODIS, and MERIS ocean colour products in the South China Sea[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 35(11-12):4252-4274.
doi: 10.1080/01431161.2014.916044
|
| 35 |
ZU TINGTING, WANG DONGXIAO, GAN JIANPING , et al, 2014. On the role of wind and tide in generating variability of Pearl River plume during summer in a coupled wide estuary and shelf system[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 136:65-79.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmarsys.2014.03.005
|
 )
)
 )
)