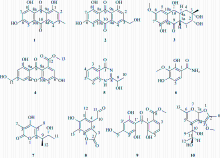
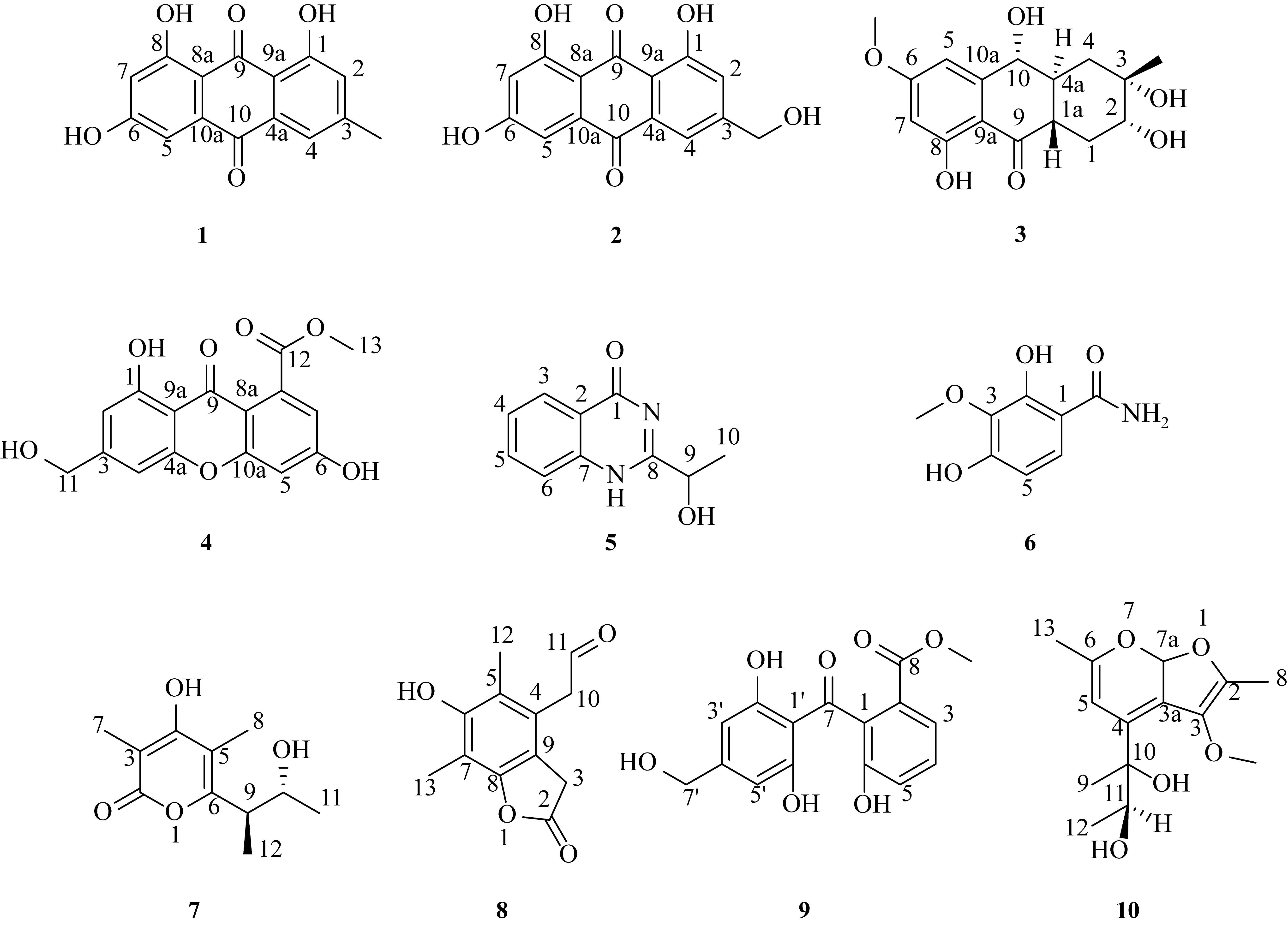
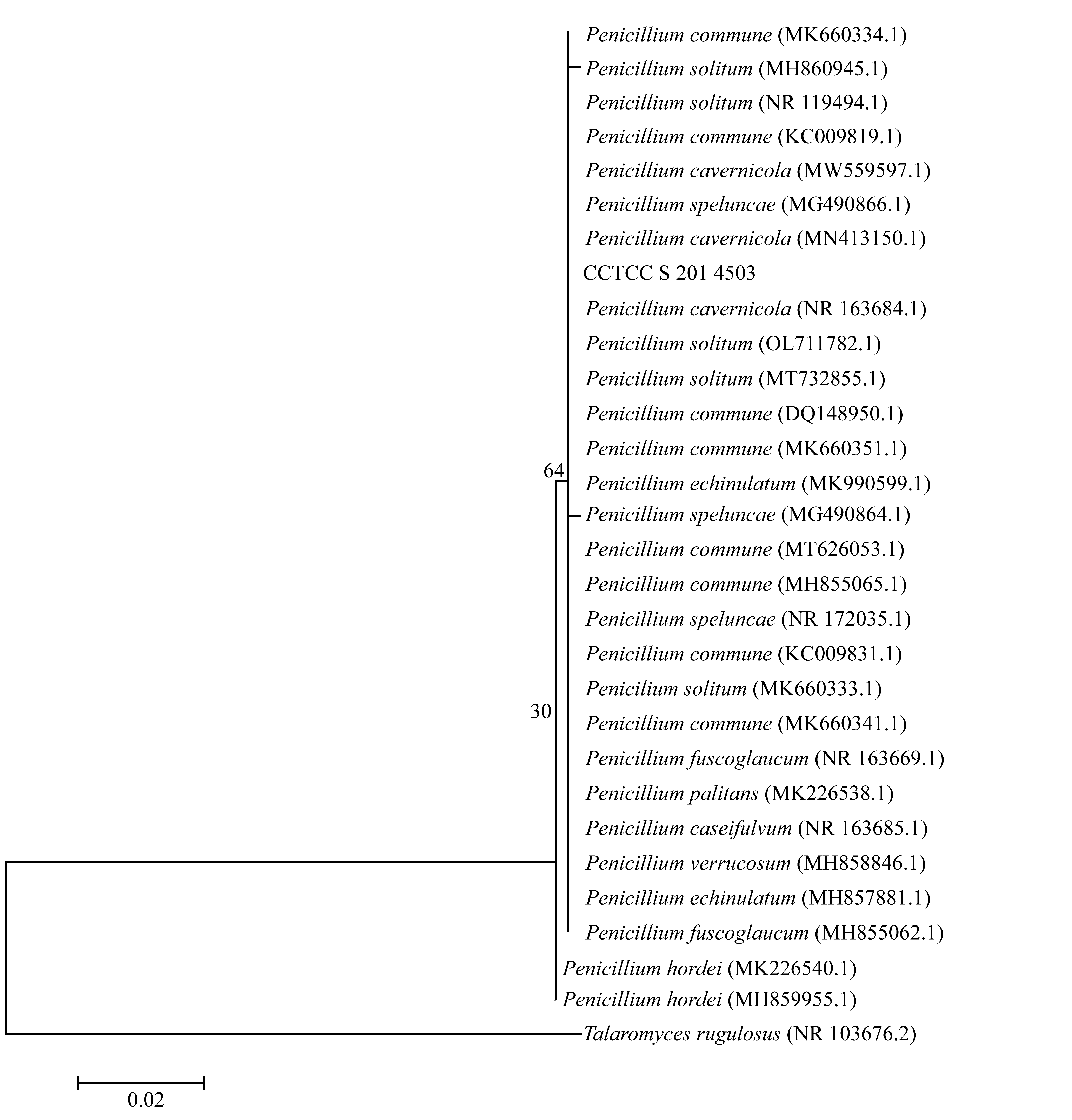
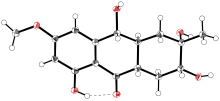
| [1] |
黄筱娟, 陈文豪, 纪明慧, 等, 2015. 菠萝叶的化学成分及生物活性研究[J]. 中草药, 46(7): 949-954.
|
|
HUANG XIAOJUAN, CHEN WENHAO, JI MINGHUI, et al, 2015. Chemical constituents from leaves of ananas comosus and their biological activities[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 46(7): 949-954. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [2] |
王淑玲, 孙云廷, 刘昱霞, 等, 2007. 大黄素的药理学研究近况[J]. 中成药, 29(6): 877-879. (in Chinese)
|
| [3] |
徐燕, 田沙沙, 朱华结, 2015. 海洋真菌灰黄青霉Penicillium griseofulvum次级代谢产物中一个新的内酯醛结构[J]. 天然产物研究与开发, 27(4): 559-561.
|
|
XU YAN, TIAN SHASHA, ZHU HUAJIE, 2015. A new lactone aldehyde compound isolated from secondary metabolites of marine fungus Penicillium griseofulvum[J]. Natural Product Research And Development, 27(4): 559-561. (in Chinese with English abstract)
|
| [4] |
杨修伟, 古哲明, 马朝梅, 等, 1998. 从何首乌根中分离的一个新的吲哚衍生物[J]. 中草药, 29(1): 5-11.
|
|
YANG XIUWEI, GU ZHEMING, MA CHAOMEI, et al, 1998. A new indole derivative isolated from the root of tuber fleeceflower (Polygonum multiflorum)[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 29(1): 5-11 (in English with Chinese abstract).
|
| [5] |
CARROLL A R, COPP B R, DAVIS R A, et al, 2022. Marine natural products[J]. Natural Product Reports, 37(2): 175-223. DOI: 10.1039/d1np00076d.
doi: 10.1039/d1np00076d
|
| [6] |
CHENG XIA, LIANG XIAO, ZHENG ZHI-HUI, et al, 2020. Penicimeroterpenoids a-c, meroterpenoids with rearrangement skeletons from the marine-derived fungus Penicillium sp. SCSIO 41512[J]. Organic Letters, 22(16): 6330-6333.
doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.0c02160
|
| [7] |
CIMMINO A, ANDOLFI A, ZONNO M C, et al, 2013. Chenopodolans A-C: phytotoxic furopyrans produced by Phoma chenopodiicola, a fungal pathogen of Chenopodium album[J]. Phytochemistry, 96: 208-213.
doi: 10.1016/j.phytochem.2013.10.007
|
| [8] |
COCKERILL F R, WIKLER M A, BUSH K, et al, 2010. Performance standards for antimicrobial disk susceptibility testing, Twentieth informational supplement[M]. CLSI document M100-S20 (ISBN 1-56238-716-2), Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, Pennsylvania 19087-1898 USA.
|
| [9] |
DAYALAN S A J, DARWIN P, PRAKASH S, 2011. Comparative study on production, purification of penicillin by Penicillium chrysogenum isolated from soil and citrus samples[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine, 1(1): 15-19.
doi: 10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60061-0
|
| [10] |
DOLOMANOV O V, BOURHIS L J, GILDEA R J, et al, 2009. OLEX2: a complete structure solution, refinement and analysis program[J]. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 42(2): 339-341.
doi: 10.1107/S0021889808042726
|
| [11] |
KETTERING M, STERNER O, ANKE T, 2004. Antibiotics in the chemical communication of fungi[J]. Zeitschrift Für Naturforschung C, 59(11-12): 816-823.
doi: 10.1515/znc-2004-11-1209
|
| [12] |
KORNSAKULKARN J, SAEPUA S, KOMWIJIT S, et al, 2014. Bioactive polyketides from the fungus Astrocystis sp. BCC 22166[J]. Tetrahedron, 70(12): 2129-2133.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2014.02.004
|
| [13] |
LIBERRA K, LINDEQUIST U, 1995. Marine fungi - a prolific resource of biologically active natural products?[J]. Pharmazie, 50(9): 583-588.
|
| [14] |
MARCHESE P, MAHAJAN N, O'CONNELL E, et al, 2020. A novel high-throughput screening platform identifies itaconate derivatives from marine Penicillium antarcticum as inhibitors of mesenchymal stem cell differentiation[J]. Marine Drugs, 18(4): 192.
doi: 10.3390/md18040192
|
| [15] |
NGAN N T T, QUANG T H, KIM K W, et al, 2017. Anti-inflammatory effects of secondary metabolites isolated from the marine-derived fungal strain Penicillium sp. SF-5629[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research, 40(3): 328-337.
doi: 10.1007/s12272-017-0890-5
|
| [16] |
OKAMURA N, MIMURA K, HARAGUCHI H, et al, 1996. Altersolanol-related compounds from the culture liquid of Alternaria solani[J]. Phytochemistry, 42(1): 77-80.
doi: 10.1016/0031-9422(95)00861-6
|
| [17] |
PANG XIAOYAN, CAI GUODI, LIN XIUPING, et al, 2019. New alkaloids and polyketides from the marine sponge-derived fungus penicillium sp. SCSIO41015[J]. Marine Drugs, 17(7): 398.
doi: 10.3390/md17070398
|
| [18] |
PITT J L, SAMSON R A, FRISVAD J C, 2000. List of accepted species and their synonyms in the family trichocomaceae[M]. Harwood Academic Publishers:9-46.
|
| [19] |
RAJABI S, RAMAZANI A, HAMIDI M, et al, 2015. Artemia salina as a model organism in toxicity assessment of nanoparticles[J]. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 23(1): 20.
doi: 10.1186/s40199-015-0105-x
|
| [20] |
SHAABAN K A, SHEPHERD M D, AHMED T A, et al, 2012. Pyramidamycins A-D and 3-hydroxyquinoline-2-carboxamide; cytotoxic benzamides from Streptomyces sp. DGC1[J]. Journal of Antibiotics, 65(12): 615-622.
doi: 10.1038/ja.2012.81
|
| [21] |
SHELDRICK G, 2015a. SHELXT-integrated space-group and crystal-structure determination[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section A Found Adv, 71(1): 3-8.
doi: 10.1107/S2053273314026370
|
| [22] |
SHELDRICK G M, 2015b. Crystal structure refinement with SHELXL[J]. Acta Crystallographica Section C-Structural Chemistry, 71(Pt 1): 3-8.
doi: 10.1107/S2053229614024218
|
| [23] |
TAMURA K, NEI M, KUMAR S, 2004. Prospects for inferring very large phylogenies by using the neighbor-joining method[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(30): 11030-11035.
doi: 10.1073/pnas.0404206101
pmid: 15258291
|
| [24] |
TANG TIAN, YIN LONGWU, YANG JING, et al, 2007. Emodin, an anthraquinone derivative from rheum officinale baill, enhances cutaneous wound healing in rats[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology, 567(3): 177-185.
pmid: 17540366
|
| [25] |
TSANTRIZOS Y S, XU XIAOJING, SAURIOL F, et al, 1994. Novel quinazolinones and enniatins from fusarium lateritium nees[J]. Canadian Journal of Chemistry-Revue Canadienne De Chimie, 72(5): 1415-1415.
doi: 10.1139/v94-177
|
| [26] |
WANG YINCHAO, ZHENG ZHIHUI, LIU SHUCHUN, et al, 2010. Oxepinochromenones, furochromenone, and their putative precursors from the endolichenic fungus Coniochaeta sp.[J]. Journal of Natural Products, 73(5): 920-924.
doi: 10.1021/np100071z
|
| [27] |
WELLS J M, COLE R J, KIRKSEY J W, 1975. Emodin, a toxic metabolite of aspergillus wentii isolated from weevil-damaged chestnuts[J]. Appllied Microbiology, 30(1): 26-28.
|
| [28] |
WU GUANGWEI, MA HONGYAN, ZHU TIANJIAO, et al, 2012. Penilactones A and B, two novel polyketides from Antarctic deep-sea derived fungus Penicillium crustosum PRB-2[J]. Tetrahedron, 68(47): 9745-9749.
doi: 10.1016/j.tet.2012.09.038
|
 ), IMRAN Khan1,2, KUMAR Saurav4, 张丽萍1,3, 方壮杰1,2, 张鑫雅1,2, 彭方5, 张长生1,2,3
), IMRAN Khan1,2, KUMAR Saurav4, 张丽萍1,3, 方壮杰1,2, 张鑫雅1,2, 彭方5, 张长生1,2,3
 ), IMRAN Khan1,2, KUMAR Saurav4, ZHANG Liping1,3, FANG Zhuangjie1,2, ZHANG Xinya1,2, PENG Fang5, ZHANG Changsheng1,2,3
), IMRAN Khan1,2, KUMAR Saurav4, ZHANG Liping1,3, FANG Zhuangjie1,2, ZHANG Xinya1,2, PENG Fang5, ZHANG Changsheng1,2,3