热带海洋学报 ›› 2023, Vol. 42 ›› Issue (2): 153-168.doi: 10.11978/2022096CSTR: 32234.14.2022096
基于高分光学与全极化SAR的海南八门湾红树林种间分类方法
张程飞1,2( ), 任广波2, 吴培强2(
), 任广波2, 吴培强2( ), 胡亚斌2, 马毅2, 阎宇3, 张菁锐4
), 胡亚斌2, 马毅2, 阎宇3, 张菁锐4
- 1.山东科技大学测绘与空间信息学院, 山东 青岛 266590
2.自然资源部第一海洋研究所, 山东 青岛 266061
3.国家卫星海洋应用中心, 北京 100081
4.中国石油大学(华东)海洋与空间信息学院, 山东 青岛 266580
-
收稿日期:2022-05-03修回日期:2022-07-05出版日期:2023-03-10发布日期:2022-07-11 -
通讯作者:吴培强。email:wu1416@163.com -
作者简介:张程飞(1998—), 男, 硕士研究生, 主要从事红树林遥感监测研究。email: zcf199828@163.com
-
基金资助:国家自然科学基金项目(42106179); 自然资源卫星遥感业务支持服务体系项目(121168000000190033); 高分海洋资源环境遥感信息处理与业务应用示范系统(二期)项目(41-Y30F07-9001-20/22)
Mangrove species classification in the Hainan Bamen Bay based on GF optics and fully polarimetric SAR
ZHANG Chengfei1,2( ), REN Guangbo2, WU Peiqiang2(
), REN Guangbo2, WU Peiqiang2( ), HU Yabin2, MA Yi2, YAN Yu3, ZHANG Jingrui4
), HU Yabin2, MA Yi2, YAN Yu3, ZHANG Jingrui4
- 1. College of Geodesy and Geomatics, Shandong University of Science and Technology, Qingdao 266590, China
2. The First Institute of Oceanography, Ministry of Natural Resources, Qingdao 266061, China
3. National Satellite Marine Application Center, Beijing 100081, China
4. College of Oceanography and Space Informatics, China University of Petroleum, Qingdao 266580, China
-
Received:2022-05-03Revised:2022-07-05Online:2023-03-10Published:2022-07-11 -
Contact:WU Peiqiang. email:wu1416@163.com -
Supported by:National Natural Science Foundation of China(42106179); Natural Resources Satellite Remote Sensing Operational Service System(121168000000190033); High Resolution Marine Resources and Environment Remote Sensing Information Processing and Business Application Demonstration System (Phase Ⅱ)(41-Y30F07-9001-20/22)
摘要:
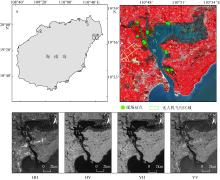
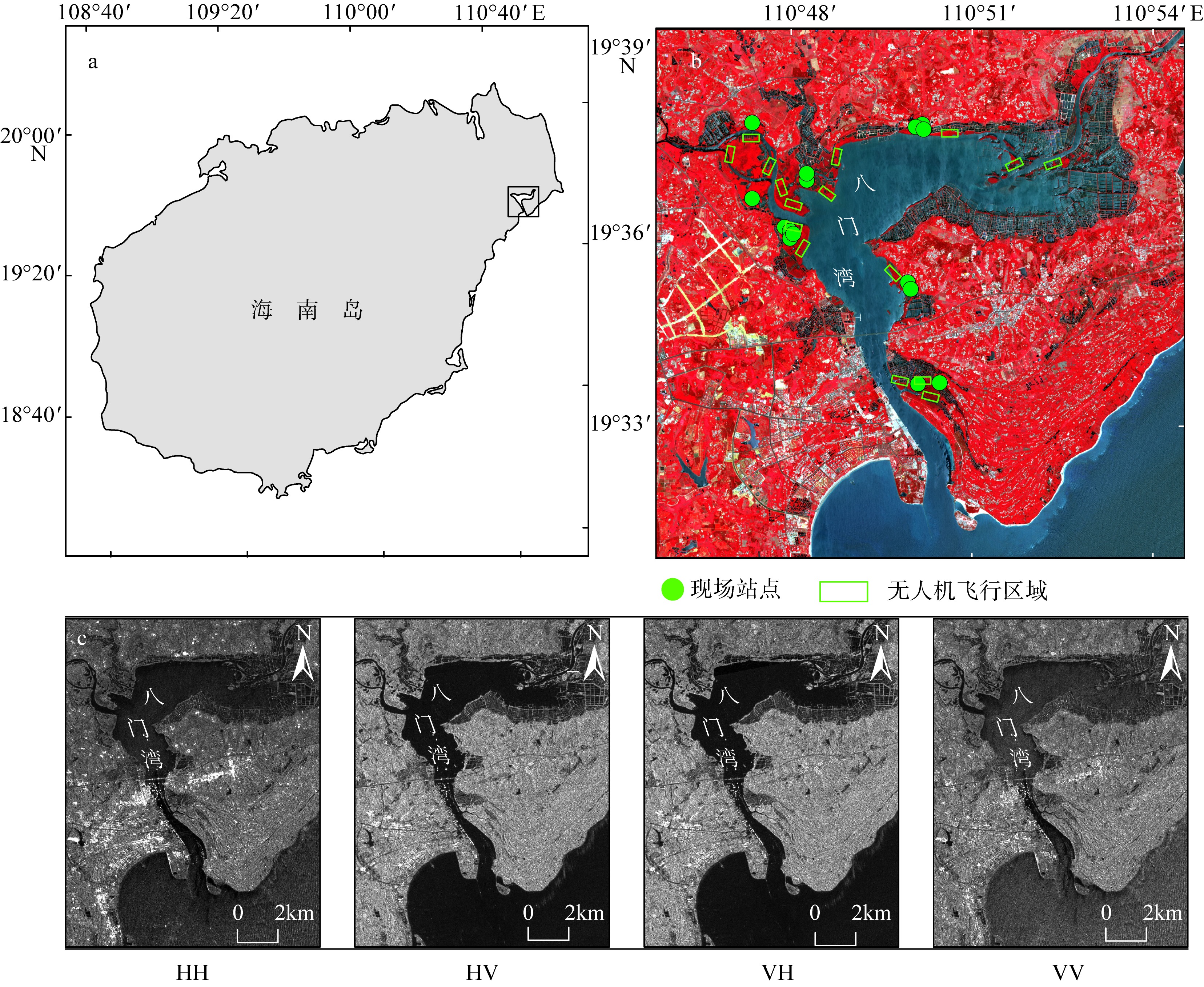
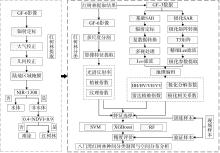
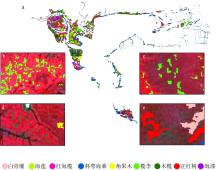
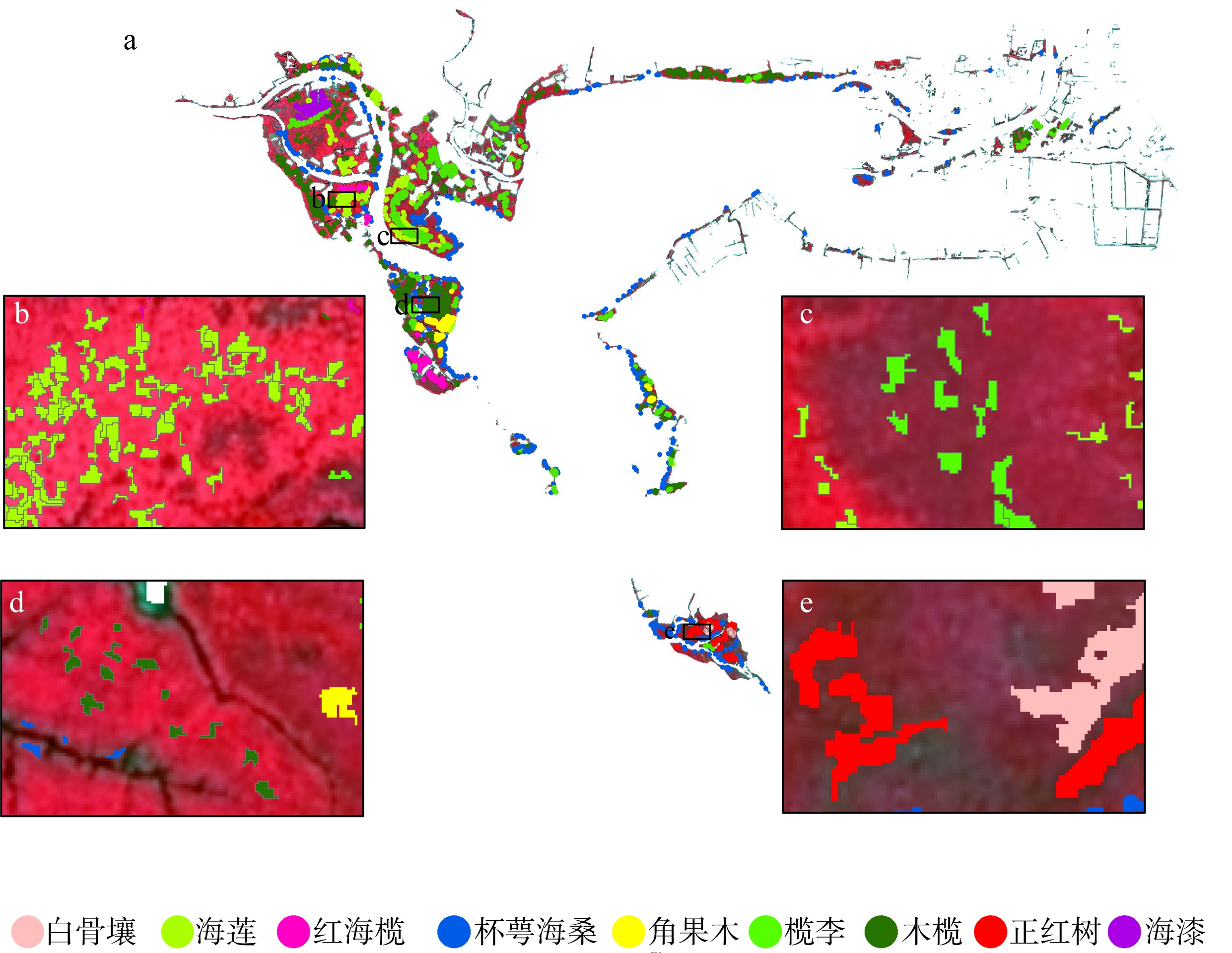
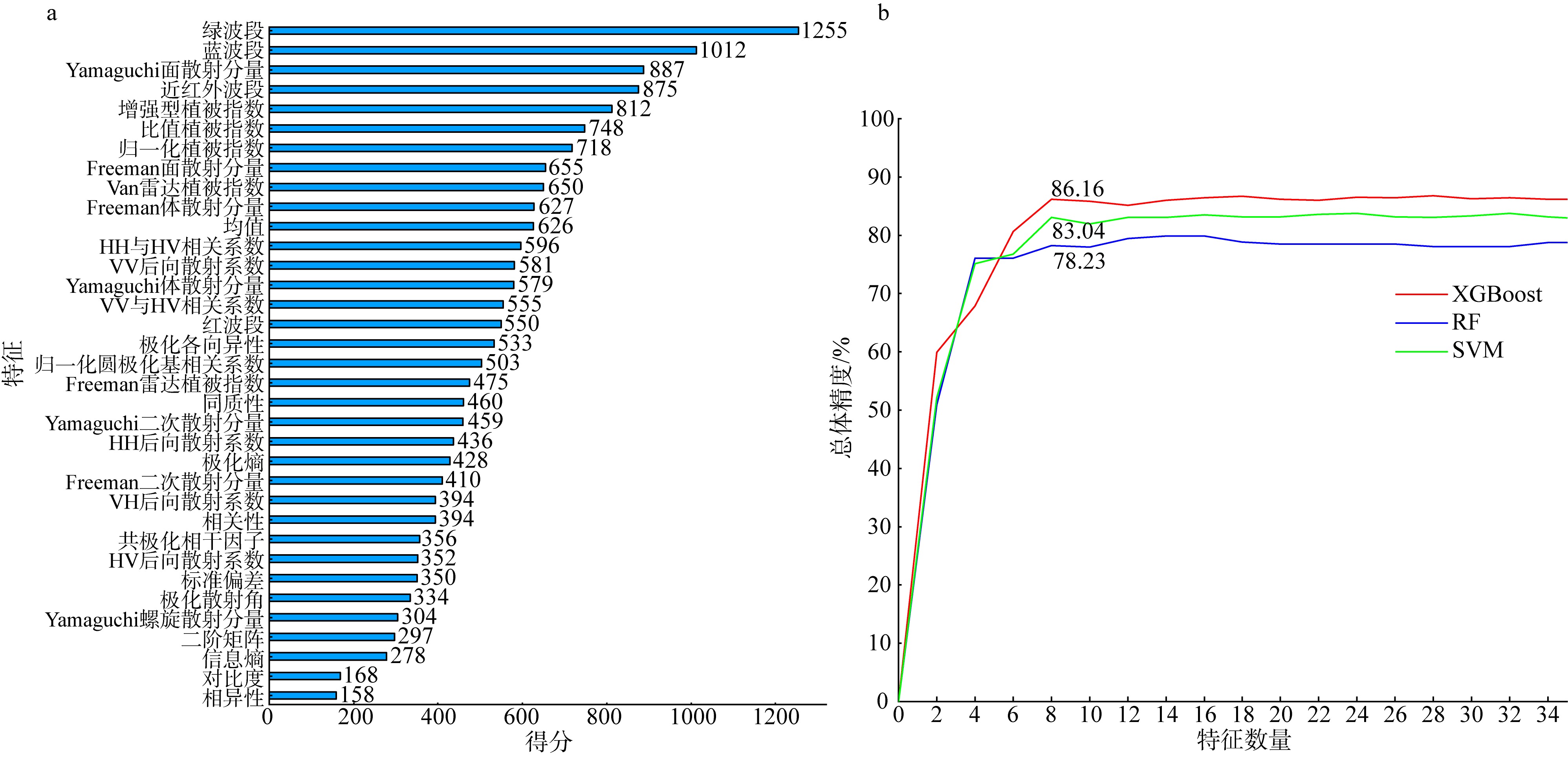
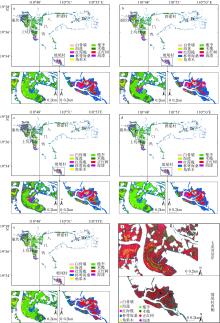
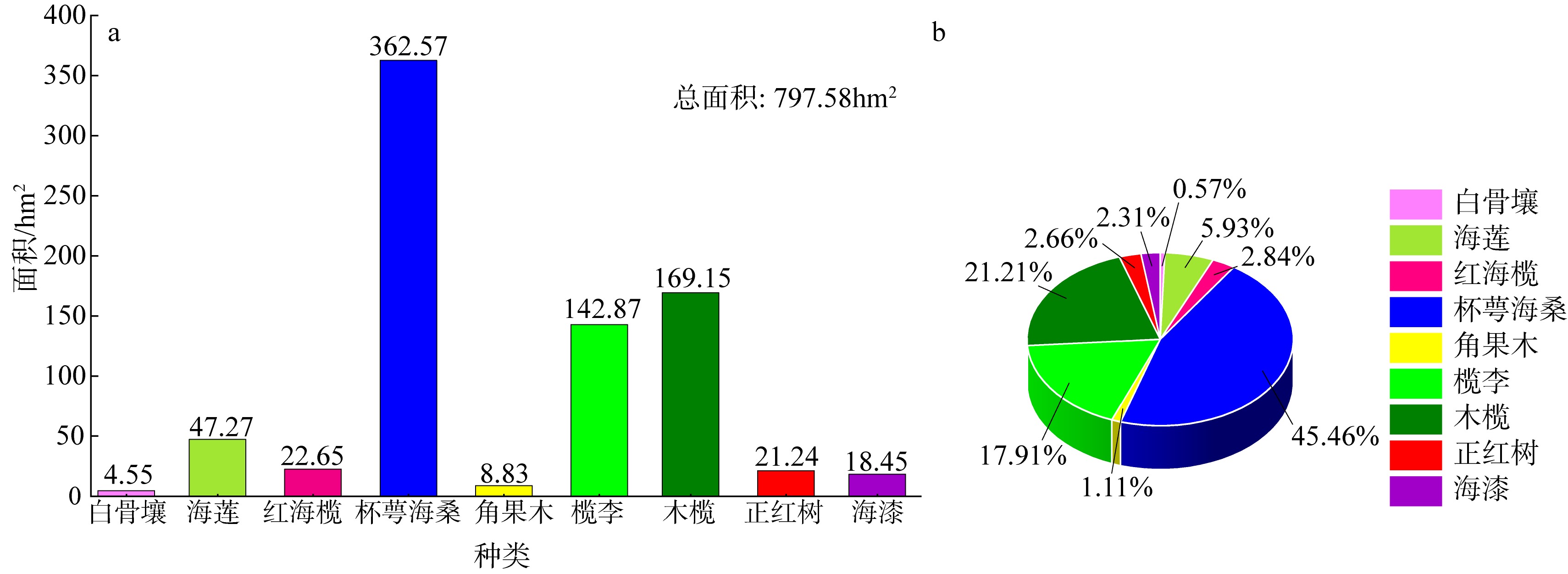
合理的红树种间组成结构是有效发挥红树林湿地生态价值的前提, 明确的红树林种间分布信息是开展红树林生态系统治理和规划工作的有效依据。针对海南八门湾红树林湿地, 基于高分三号(GF-3)全极化合成孔径雷达(synthetic aperture radar, SAR)和高分六号(GF-6)多光谱遥感数据, 本文提取了35个红树林遥感特征, 利用极端梯度提升树(eXtreme gradient boosting, XGBoost)算法开展了特征重要性排序、特征筛选和红树林种间分类实验, 将其与传统的支持向量机(support vector machine, SVM)、随机森林(random forest, RF)机器学习算法进行精度比较, 并基于XGBoost算法进行了3种特征组合方式(优选特征、多光谱特征、全极化SAR特征)的分类精度比较, 旨在探索XGBoost对红树林种间分类的适用性和光学与全极化SAR数据对红树林种间分类的能力。结果表明: 1) 识别红树林种类的优势特征依次为多光谱的光谱波段、极化分解参数、光谱植被指数, 且仅利用前8个优选特征(绿光波段反射率G、蓝光波段反射率B、Yamaguchi面散射分量Ys、近红外波段反射率NIR、增强型植被指数EVI、比值植被指数RVI、归一化植被指数NDVI、Freeman面散射分量Fs)即可达到较高分类精度。2) 对于八门湾红树林湿地, XGBoost算法的红树种间分类总体精度最高, 为86.16%, 卡帕系数为0.836, 比SVM和RF算法高3% ~ 8%; 优选特征的红树林种间分类精度比单独的多光谱特征或全极化SAR特征高10% ~ 12%。3) 八门湾红树林总面积约为797.58hm2, 共有白骨壤、海莲、红海榄、杯萼海桑、角果木、榄李、木榄、正红树、海漆9种优势真红树, 杯萼海桑和木榄的面积较大, 分别占全部红树林面积的45.46%、21.21%。
引用本文
张程飞, 任广波, 吴培强, 胡亚斌, 马毅, 阎宇, 张菁锐. 基于高分光学与全极化SAR的海南八门湾红树林种间分类方法[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(2): 153-168.
ZHANG Chengfei, REN Guangbo, WU Peiqiang, HU Yabin, MA Yi, YAN Yu, ZHANG Jingrui. Mangrove species classification in the Hainan Bamen Bay based on GF optics and fully polarimetric SAR[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2023, 42(2): 153-168.
表2
红树林类型及遥感影像解译描述"
| 红树种类 | 现场照片 | GF-6影像 | GF-3影像 | 红树属性及影像特征 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 白骨壤(Avicennia marina) | | | | 小叶、耐盐、耐淹、常绿灌木或小乔木、常分布于淡水注入较少的海湾区域。影像纹理略粗糙, 色调较均一, GF-6影像为暗红色, GF-3影像为紫色 |
| 海莲(Bruguiera sexangula) | | | | 木榄属乔木或灌木, 生于滨海盐滩或潮水到达的沼泽地。影像纹理较平滑, 色调较均一, GF-6影像为亮红色, GF-3影像为白色 |
| 红海榄(Rhizophora stylosa Griff) | | | | 支柱根、常绿乔木或灌木、较耐盐、多分布于河口外侧盐度较高的红树林内滩。影像纹理粗糙, 色调略杂乱, GF-6影像为暗红色, GF-3影像为紫色 |
| 杯萼海桑(Sonneratia alba Sm) | | | | 海桑属灌木或乔木, 生于滨海泥滩和河流两侧而潮水到达的红树林群落中。影像纹理粗糙, 色调较均一, GF-6影像为暗红色中掺杂白色斑点, GF-3影像为灰绿色 |
| 角果木(Ceriops tagal) | | | | 灌木或乔木, 耐盐性较强, 生于潮涨时仅淹没树干基部的泥滩和海湾内的沼泽地。影像纹理平滑细腻, 色调均一, GF-6影像为暗红色, GF-3影像浅红色 |
| 木榄(Bruguiera gymnorrhiza) | | | | 常绿乔木或灌木, 耐淹能力较差、多分布于红树林内滩。影像纹理略粗糙, 色调较均一, GF-6影像为亮红色, GF-3影像为灰绿色 |
| 榄李(Lumnitzera racemosa Willd) | | | | 使君子科、榄李属常绿灌木或小乔木, 喜生于中潮滩或高潮滩。影像纹理较平滑, 色调均一, GF-6影像为暗红色, GF-3影像为浅紫色 |
| 正红树(Rhizophora apiculata Bl) | | | | 常绿小乔木或灌木, 分布于海浪平静、淤泥松软的浅海盐滩或海湾内的沼泽地。影像纹理平滑, 色调均一, GF-6影像为深红色, GF-3影像为蓝色 |
| 海漆(Excoecaria agallocha Linn) | | | | 大戟科海漆属植物, 常绿乔木, 生于海陆交错区的高潮带或超高潮带的盐碱地上。影像纹理略粗糙, 色调较均一, GF-6影像为浅红色, GF-3影像为蓝绿色 |
表3
GF-6多光谱特征"
| 遥感特征 | 名称 | 公式 | 出处 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 光谱波段反射率 | B1 ~ B4 | — | |
| 植被指数 | 归一化植被指数(NDVI) | Rouse等( | |
| 增强型植被指数(enhanced vegetation index, EVI) | Liu等( | ||
| 比值植被指数(ratio vegetation index, RVI) | Pearson等( | ||
| 纹理参数 | 相关性(correlation) | Haralick等( | |
| 同质性(homogeneity) | |||
| 对比度(contrast) | |||
| 标准偏差(standard deviation) | |||
| 二阶矩阵(second moment) | |||
| 相异性(dissimilarity) | |||
| 均值(mean) | |||
| 信息熵(entropy) |
表4
GF-3全极化SAR特征"
| 遥感特征 | 名称 | 公式 | 出处 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 极化图像波段特征 | HH/HV/VH/VV | / / / | Souyris等( | |
| 极化相关特征 | 共极化相干因子(polcoe) | Henderson等( | ||
| HH与HV相关系数 (ρHH-HV) | Souyris等( | |||
| VV与HV相关系数 (ρVV-HV) | Souyris等( | |||
| 归一化圆极化基相关系数(NCCC) | 杨杰等( | |||
| 极化分解特征 | Freeman分解 | 体散射分量 (Freeman_vol, Fv) | Freeman等( | |
| 二次散射分量(Freeman_dbl, Fd) | ||||
| 面散射分量 (Freeman_surf, Fs) | ||||
| 雷达植被指数(RVI_Freeman) | ||||
| Yamaguchi分解 | 体散射分量(Yamaguchi_vol, Yv) | Yamaguchi等( | ||
| 二次散射分量(Yamaguchi_dbl, Yd) | ||||
| 面散射分量(Yamaguchi_surf, Ys) | ||||
| 螺旋散射分量(Yamaguchi_cir, Yc) | ||||
| H/A/ 分解 | 极化熵H (entropy) | Cloude等( | ||
| 极化各向异性A (anisotropy) | ||||
| 极化散射角 (alpha) | ||||
| Van雷达植被指数(RVI_Van) | Zyl等( | |||
表5
分类精度评价"
| 支持向量机 | 随机森林 | 极端梯度提升树 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 优选特征 | 优选特征 | 优选特征 | 多光谱特征 | 全极化SAR特征 | ||||||
| PA/% | UA/% | PA/% | UA/% | PA/% | UA/% | PA/% | UA/% | PA/% | UA/% | |
| 白骨壤 | 76.47 | 65.00 | 100.00 | 83.33 | 94.74 | 90.00 | 66.67 | 50.00 | 85.71 | 85.71 |
| 海莲 | 84.93 | 69.66 | 86.25 | 75.82 | 82.47 | 89.89 | 87.38 | 63.22 | 79.01 | 74.42 |
| 红海榄 | 64.86 | 63.16 | 83.33 | 65.79 | 84.38 | 71.05 | 76.67 | 50.00 | 71.05 | 62.79 |
| 杯萼海桑 | 85.71 | 80.95 | 86.51 | 85.83 | 90.60 | 84.13 | 83.78 | 80.17 | 64.23 | 69.91 |
| 角果木 | 82.19 | 88.24 | 95.00 | 98.70 | 95.59 | 95.59 | 88.16 | 89.33 | 83.16 | 90.80 |
| 榄李 | 72.73 | 74.32 | 80.55 | 83.82 | 85.48 | 86.89 | 68.06 | 77.84 | 74.25 | 76.54 |
| 木榄 | 72.67 | 78.99 | 72.39 | 82.27 | 77.30 | 78.99 | 67.84 | 81.69 | 69.28 | 65.84 |
| 正红树 | 90.20 | 97.87 | 94.87 | 90.24 | 94.00 | 100.00 | 91.67 | 89.80 | 90.00 | 91.84 |
| 海漆 | 81.08 | 85.71 | 76.66 | 74.19 | 88.24 | 85.71 | 73.33 | 64.71 | 81.82 | 69.23 |
| 总体精度/% | 78.23 | 83.04 | 86.16 | 76.22 | 74.77 | |||||
| Kappa系数 | 0.7417 | 0.9800 | 0.8359 | 0.7174 | 0.7033 | |||||
表6
各组实验的算法参数"
| 实验组别 | 算法参数 |
|---|---|
| SVM+优选特征 | Kernel Type: 'RBF' Penalty=185; gamma=0.0001 |
| RF+优选特征 | n_estimators=120; max_depth=15; max_features=8 |
| XGBoost+优选特征 | learning_rate=0.06; n_estimators=252; max_depth=5; gamma=0.2 |
| XGBoost+多光谱特征 | learning_rate=0.09; n_estimators=10; max_depth=5; gamma=0.8 |
| XGBoost+全极化SAR特征 | learning_rate=0.09; n_estimators=10; max_depth=6; gamma=0.9 |
| [1] |
杜云艳, 周成虎, 1998. 水体的遥感信息自动提取方法[J]. 遥感学报, (4): 264-269.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
范航清, 张云兰, 邹绿柳, 等, 2022. 中国红树林基准价值及其单株价值分配研究[J]. 生态学报, 42(4): 1262-1275.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
何海军, 温家声, 张锦炜, 等, 2015. 海南红树林湿地生态系统服务价值评估[J]. 生态经济, 31(4): 145-149.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李森, 蔡厚才, 陈万东, 等, 2020. 海岸带生态恢复区不同林龄红树林对CH4和CO2排放通量的影响[J]. 生态环境学报, 29(12): 2414-2422.
doi: 10.16258/j.cnki.1674-5906.2020.012.012 |
|
|
|
| [5] |
林鹏, 2001. 中国红树林研究进展[J]. 厦门大学学报(自然科学版), (2): 592-603.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
马云梅, 吴培强, 任广波, 等, 2019. 基于国产高分遥感的人工种植红树林种间分类方法研究——以广西茅尾海红树林为例[J]. 海洋技术学报, 38(4): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
马云梅, 吴培强, 任广波, 2021. 基于高分影像光谱特征的广西海岸带红树林精细分类与制图[J]. 地球信息科学学报, 23(12): 2292-2304.
doi: 10.12082/dqxxkx.2021.210494 |
|
|
|
| [8] |
农寿千, 杨小波, 李东海, 等, 2011. 清澜港红树林保护区植物特点研究[J]. 植物科学学报, 1(4): 459-466.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
任广波, 周莉, 梁建, 等, 2021. “高分五号”高光谱互花米草遥感识别与制图研究[J]. 海洋科学进展, 39(2): 312-326.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
邵永社, 韩阳, 吕倩利, 等, 2011. 4分量模型和散射参数的全极化雷达图像分类[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版), 39(9): 1345-1349.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
苏岫, 赵冬至, 黄凤荣, 等, 2011. 基于高空间分辨率的红树林卫星遥感监测技术进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 30(3): 38-45.
|
|
doi: 10.11978/j.issn.1009-5470.2011.03.038 |
|
| [12] |
涂志刚, 吴瑞, 张光星, 等, 2015. 海南岛清澜港红树植物群落类型及其特征[J]. 热带农业科学, 35(11): 21-25.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
徐晓然, 谢跟踪, 邱彭华, 2018. 1964—2015年海南省八门湾红树林湿地及其周边土地景观动态分析[J]. 生态学报, 38(20): 7458-7468.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
杨杰, 赵伶俐, 李平湘, 等, 2012. 引入规范化圆极化相关系数的保持极化散射特性的分类算法[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 37(8): 911-914.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
杨众养, 薛杨, 宿少锋, 等, 2017. 文昌市八门湾红树林区植物群落特征调查[J]. 热带农业科学, 37(1): 48-52, 59.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
郑德璋, 廖宝文, 郑松发, 等, 1995. 海南岛清澜港红树树种适应生境能力与水平分布[J]. 林业科学研究, 8(1): 67-72.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
郑艺, 林懿琼, 周建, 等, 2019. 基于资源三号的雷州半岛红树林种间分类研究[J]. 国土资源遥感, 31(3): 201-208.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
邹斌, 张腊梅, 孙德明, 等, 2009. PolSAR图像信息提取技术及应用的发展[J]. 遥感技术与应用, 24(3): 263-273.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2015.12.012 |
| [20] |
doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63880-1 |
| [21] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2008.02.011 |
| [22] |
doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtp009 |
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
doi: 10.1007/s12524-014-0392-6 |
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2019.01.019 |
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
doi: 10.1146/energy.2019.44.issue-1 |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
|
| [32] |
doi: 10.1080/0143116031000066323 |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
doi: 10.3390/rs13081529 |
| [35] |
doi: 10.3390/rs11212479 |
| [36] |
doi: 10.1016/j.rse.2021.112403 |
| [37] |
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.36 |
| [38] |
doi: 10.1093/jpe/rtq004 |
| [39] |
doi: 10.3390/rs9040342 |
| [40] |
doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-17451-0 |
| [41] |
|
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
doi: 10.3390/rs10020294 |
| [46] |
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2021.11.020 |
| [47] |
doi: 10.3390/rs12223834 |
| [48] |
doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2010.2099124 |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
doi: 10.3390/rs10030467 |
| [51] |
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3070810 |
| [52] |
doi: 10.3390/s18114012 |
| [53] |
doi: 10.1016/j.ecolind.2021.108148 |
| [54] |
|
| [1] | 吴鸿博, 罗锋, 陈治澎, 朱飞, 曾靖伟, 张弛, 李瑞杰. 红树林生态重建效果预测研究新模式[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 86-97. |
| [2] | 郑法, 黄福林, 陈泽恒, 丁伟品. 基于LUCC和景观格局变化的广西山口红树林湿地动态研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 165-173. |
| [3] | 周治刚, 岳文, 李辉权, 林阳阳. 树种类型和潮滩高程对广东湛江高桥红树林碳储量的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(2): 108-120. |
| [4] | 申键, 简焯锴, 欧阳雪敏, 艾彬. 结合潮位校正的雷州半岛红树林湿地动态变迁遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 137-153. |
| [5] | 耿婉璐, 邢永泽, 张秋丰, 管卫兵. 广西北海红树林宜林滩涂大型底栖动物群落结构特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(1): 107-115. |
| [6] | 董俊德, 黄小芳, 龙爱民, 王友绍, 凌娟, 杨清松. 红树林固氮微生物及其生态功能研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 1-11. |
| [7] | 梁寒峭, 陈文凤, 范益铠, 朱子冬, 马国需, 陈德力, 田婧. 红树林来源曲霉属和木霉属内生真菌次生代谢产物及活性研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(4): 12-24. |
| [8] | 周月月, 王友绍. 广东沿海红树林区水质变化特征与富营养状态评估[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 1-11. |
| [9] | 吴伟志, 赵志霞, 杨升, 梁立成, 陈秋夏, 卢翔, 刘星, 张小伟. 浙江省红树林分布和造林成效分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 67-74. |
| [10] | 郝露露, 柯明思, 朱奕秀, 许燕敏, 张颖, 郑春芳. 低温胁迫下红榄李(Lumnitzera littorea)DEAD-box RNA解旋酶基因的表达分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(6): 44-55. |
| [11] | 李华薇, 徐向荣. 中国典型红树林沉积物中多溴联苯醚和替代型溴系阻燃剂污染特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 117-130. |
| [12] | 王友绍. 全球气候变化对红树林生态系统的影响、挑战与机遇[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 1-14. |
| [13] | 戴志军, 周晓妍, 王杰, 胡宝清. 红树林潮滩沉积动力研究进展与展望[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 69-75. |
| [14] | 董迪, 曾纪胜, 魏征, 严金辉. 联合星载光学和SAR影像的漳江口红树林与互花米草遥感监测[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(2): 107-117. |
| [15] | 李小维, 黄子眉, 陈剑锋, 王欣, 韦江玲. 基于VSD模型的铁山港湾红树林生态系统脆弱性初步评价[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(2): 47-54. |
|
||