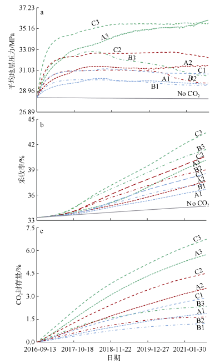
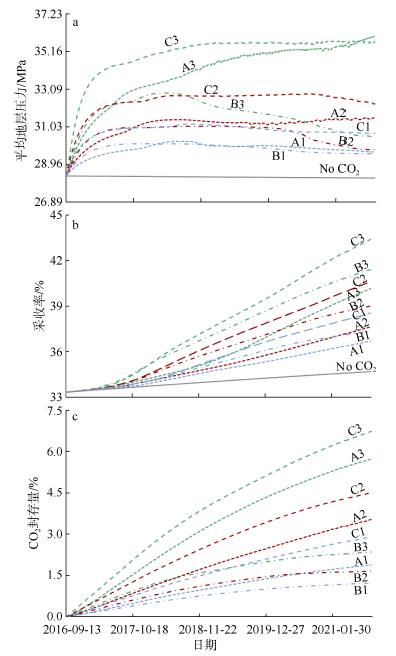
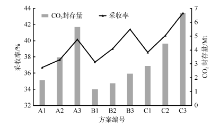
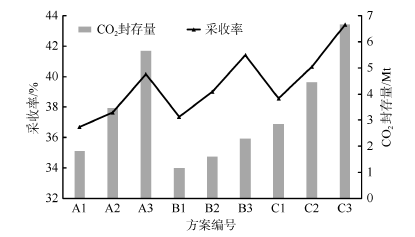
| [1] |
毕凤琴, 李芳, 梁辉, 2011.“CO2-EOR”技术的国内外研究及应用现状[J]. 价值工程, 30(11): 206-207.
|
|
BI FENGQIN, LI FANG, LIANG HUI, 2011. Domestic and foreign research and application progress on CO2-EOR technology[J]. Value Engineering, 30(11): 206-207 (in Chinese).
|
| [2] |
陈澜, 梁希, 周蒂, 2014. 发展碳捕集、利用与封存对广东的产业机会[J]. 南方能源建设, 1(1): 7-15.
|
|
CHEN LAN, LIANG XI, ZHOU DI, 2014. Potential economic opportunities of developing a CCUS industry in Guangdong[J]. Energy Construction, 1(1): 7-15 (in Chinese).
|
| [3] |
陈维涛, 杜家元, 龙更生, 等, 2012. 珠江口盆地惠州地区珠江组控砂机制及地层-岩性圈闭发育模式[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 33(3): 449-458.
|
|
CHEN WEITAO, DU JIAYUAN, LONG GENGSHENG, et al, 2012. Factors controlling sandbody development and models of stratigraphic-lithologic traps of Zhujiang Formation in Huizhou area, Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 33(3): 449-458 (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
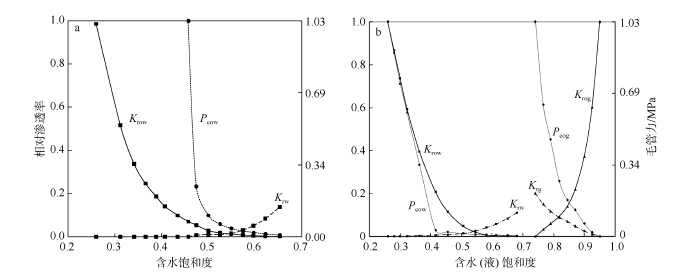
杜宗君, 张荣明, 2000. 应用测井资料结合岩相计算储层渗透率[J]. 测井技术, 24(增): 521-523.
|
|
DU ZONGJUN, ZHANG RONGMING, 2000. Calculation of reservoir permeability using log data and litho-facies[J]. Well Logging Technology, 24(Suppl): 521-523 (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
郝敏, 宋永臣, 2010. 利用CO2提高石油采收率技术研究现状[J]. 钻采工艺, 33(4): 59-63. HAO MIN, SONG YONGCHEN, 2010. Research status of CO2-EOR[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 33(4): 59-63 (in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
雷霄, 胡余, 梁文锋, 等, 2015. 文昌19-1油田珠江组二段Ⅰ油组沉积相研究[J]. 西南石油大学学报(自然科学版), 37(4): 1-12.
|
|
LEI XIAO, HU YU, LIANG WENFENG, et al, 2015. A Study on Sedimentary Facies of Oil Group I in Member 2 of Zhujiang Formation in Wenchang 19-1 Oilfield[J]. Journal of Southwest Petroleum University (Science & Technology Edition), 37(4): 1-12 (in Chinese).
|
| [7] |
刘恒, 高树堂, 1995. 大庆油田开发先导性矿场试验[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [8] |
罗二辉, 胡永乐, 李保柱, 等, 2013. 中国油气田注CO2提高采收率实践[J]. 特种油气藏, 20(2): 1-7.
|
|
LUO ERHUI, HU YONGLE, LI BAOZHU, et al, 2013. Practices of CO2 EOR in China[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 20(2): 1-7 (in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
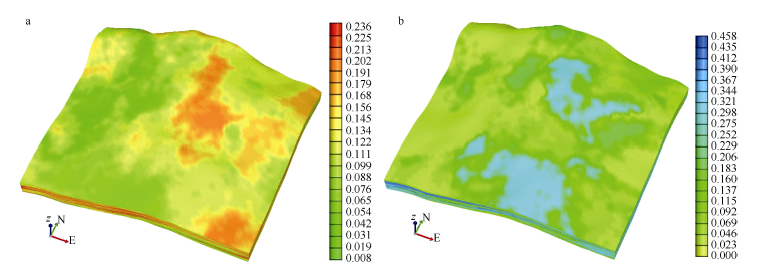
彭佳龙, 陈广浩, 周蒂, 等, 2013. 珠江口盆地惠州21-1构造二氧化碳地质封存数值模拟[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 29(9): 59-70.
|
|
PENG JIALONG, CHEN GUANGHAO, ZHOU DI, et al, 2013. Numerical simulation for offshore storage of carbon dioxide in Huizhou 21-1 trap, Pearl River Mouth Basin, China[J]. Marine Geology Frontiers, 29(9): 59-70 (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
秦积舜, 韩海水, 刘晓蕾, 2015. 美国CO2驱油技术应用及启示[J]. 石油勘探与开发, 42(2): 209-216.
|
|
QIN JISHUN, HAN HAISHUI, LIU XIAOLEI, 2015. Application and enlightenment of carbon dioxide flooding in the United States of America[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development, 42(2): 209-216 (in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
沈平平, 江怀友, 陈永武, 等, 2007. CO2注入技术提高采收率研究[J]. 特种油气藏, 14(3): 1-4, 11, 104.
|
|
SHEN PINGPING, JIANG HUAIYOU, CHEN YONGWU, et al, 2007. EOR study of CO2 injection[J]. Special Oil and Gas Reservoirs, 14(3): 1-4, 11, 104 (in Chinese).
|
| [12] |
沈平平, 廖新维, 2009. 二氧化碳地质埋存与提高石油采收率技术[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [13] |
施和生, 于兴河, 1999. 珠江口盆地(东部)砂岩油田沉积相研究及其应用[J]. 中国海上油气(地质), 13(3): 181-188.
|
|
SHI HESHENG, YU XINGHE, 1999. A study on sedimentary facies of sandstone oil fields in eastern Pearl River Mouth Basin[J]. China Offshore Oil and Gas (Geology), 13(3): 181-188 (in Chinese).
|
| [14] |
孙枢, 2006. CO2地下封存的地质学问题及其对减缓气候变化的意义[J]. 中国基础科学, 8(3): 17-22.
|
|
SUN SHU, 2006. Geological problems of CO2 underground storage and its significance on mitigating climate change[J]. China Basic Science, 8(3): 17-22 (in Chinese).
|
| [15] |
翟光明, 王善书, 1990. 中国石油地质志: 卷十六: 沿海大陆架及毗邻海域油气区(下)[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [16] |
张晓宇, 成建梅, 刘军, 等, 2006. CO2地质处置研究进展[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 33(4): 85-89.
|
|
ZHANG XIAOYU, CHENG JIANMEI, LIU JUN, et al, 2006. An overview of underground sequestration of carbon dioxide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 33(4): 85-89 (in Chinese).
|
| [17] |
周蒂, 2005. CO2的地质存储——地质学的新课题[J]. 自然科学进展, 15(7): 782-787.
|
| [18] |
祝春生, 程林松, 2007. 低渗透油藏CO2驱提高原油采收率评价研究[J]. 钻采工艺, 30(6): 55-57.
|
|
ZHU CHUNSHENG, CHENG LINSONG, 2007. Research on CO2 flooding in low permeability reservoir[J]. Drilling & Production Technology, 30(6): 55-57 (in Chinese).
|
| [19] |
朱伟林, 米立军, 2010. 中国海域含油气盆地图集[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [20] |
《中国油气田开发志》总编纂委员会, 2013. 中国油气田开发志——南海东部油气区油气田卷[M]. 北京: 石油工业出版社.
|
| [21] |
AZZOLINA N A, NAKLES D V, GORECKI C D, et al, 2015. CO2 storage associated with CO2 enhanced oil recovery: A statistical analysis of historical operations[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 37: 384-397.
|
| [22] |
FERTL W H, FROST E JR, 1980. Evaluation of shaly clastic reservoir rocks[J]. Journal of Petroleum Technology, 32(9): 1641-1646.
|
| [23] |
ETTEHADTAVAKKOL A, LAKE L W, BRYANT S L, 2014. CO2-EOR and storage design optimization[J]. International Journal of Greenhouse Gas Control, 25: 79-92.
|
| [24] |
HILL B, HOVORKA S, MELZER S, 2013. Geologic carbon storage through enhanced oil recovery[J]. Energy Procedia, 37: 6808-6830.
|
| [25] |
IPCC, 2014. Climate Change 2014: Synthesis Report. Contribution of Working Groups I, II and III to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change[R]. Geneva: IPCC: 1-151.
|
| [26] |
JIAO Z S, ZHOU L F, GAO R M, et al, 2014. Opportunity and challenges of integrated enhanced oil recovery using CO2 flooding with geological CO2 storage in the Ordos basin, China[J]. Energy Procedia, 63: 7761-7771.
|
| [27] |
KUUSKRAA V A, GODEC M L, DIPIETRO P, 2013. CO2 utilization from “next generation” CO2 enhanced oil recovery technology[J]. Energy Procedia, 37: 6854-6866.
|
| [28] |
KUUSKRAA V A, WALLACE M, 2014. CO2-EOR set for growth as new CO2 supplies emerge[J]. Oil & Gas Journal, 112(4): 92-105.
|
| [29] |
Computer Modelling Group LTD., 2015. CMG GEM User’s Guide[Z].
|
| [30] |
MOGBO O, 2011. CO2 EOR and sequestration in a depleted gas-condensate reservoir: UKNS case study[R]. SPE 150752, Abuja: Society of Petroleum Engineers: 1-17.
|
| [31] |
SCHLUMBERGER, 2015. Petrel online help and manuals[Z].
|
| [32] |
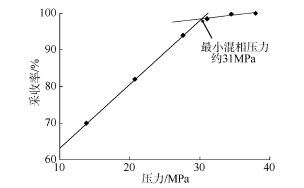
VAHIDI A, AHMADI M, NOURMOHAMMAD A, 2014. Carbon dioxide minimum miscibility pressure estimation (case study)[J]. Journal of Petroleum Science and Technology, 4(2): 20-27.
|
| [33] |
ZHAO D F, LIAO X W, YIN D D, 2014. Evaluation of CO2 enhanced oil recovery and sequestration potential in low permeability reservoirs, Yanchang Oilfield, China[J]. Journal of the Energy Institute, 87(4): 306-313.
|
 ), Pengchun LI1, Di ZHOU1, Jiemin LU3, Guanghao CHEN1
), Pengchun LI1, Di ZHOU1, Jiemin LU3, Guanghao CHEN1