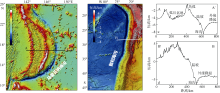
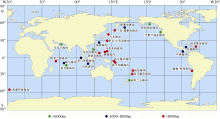
热带海洋学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 27-38.doi: 10.11978/2017012CSTR: 32234.14.2017012
海沟沉积物研究进展
- 1. 海底科学与探测技术教育部重点实验室, 中国海洋大学海洋地球科学学院, 山东 青岛266100
2. 美国伍兹霍尔海洋研究所, 马萨诸塞 伍兹霍尔02543
3. 中国科学院南海海洋研究所, 广东 广州510301
-
收稿日期:2017-01-23修回日期:2017-08-14出版日期:2017-11-30发布日期:2018-01-18 -
作者简介:作者简介:肖春晖(1991#cod#x02014;), 女, 山东省东营市人, 博士研究生, 海洋沉积学。E-mail:
chunhuixiao@qq.com -
基金资助:国家重点研发计划项目(2016YFC0402602);国家自然科学基金(41376054、41176039、41410304022、91628301、U1606401);国家海洋局公益性项目(201405037);中国科学院项目(QYZDY-SSW-DQC005、Y4SL021001)
Research progress on ocean trench sedimentation
Chunhui XIAO1( ), Yonghong WANG1(
), Yonghong WANG1( ), Jian LIN2,3
), Jian LIN2,3
- 1. Key Lab of Submarine Geosciences and Prospecting Techniques, MOE and College of Marine Geosciences, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China
2. Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution, Woods Hole, MA 02543, USA
3. South China Sea Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Guangzhou 510301, China
-
Received:2017-01-23Revised:2017-08-14Online:2017-11-30Published:2018-01-18 -
About author:Author:QIU Chunhua.E-mail:
qiuchh3@mail. sysu.edu.cn -
Supported by:National Key Research and Development Plan (2016YFC0402602);National Natural Science Foundation of China (41376054, 41176039, 41410304022, 91628301, U1606401);Public Welfare Project of the State Oceanic Administration (201405037);Chinese Academy of Sciences Project (QYZDY-SSW-DQC005, Y4SL021001)
摘要:
俯冲的大洋板块在自身的重力以及上覆板块的挤压下, 下潜时牵引洋底向下倾伏, 从而形成了深邃的海沟。板块及其所携带的沉积物在这里俯冲到地幔深处, 构成了全球物质循环的重要部分。海沟地处极端环境, 海沟沉积物的沉积作用不同于陆架和浅海地区, 其物源和水动力基本控制了沉积模式, 但海沟沉积物的物源、沉积环境和沉积机理则更为复杂。海沟沉积物受控于各种类型的构造运动, 包括由上覆板块刮削下来的深海沉积物和洋壳碎片堆积而成的沉积增生楔; 由海沟重力滑塌、地震等因素引发的浊流沉积; 以及由火山活动带来的火山物质等。同时, 海沟沉积物也受控于海沟逐渐形成过程中和形成后的各种沉积作用, 例如生物化学沉积和漏斗效应。由于海沟沉积物的沉积过程受到漏斗效应的影响, 使得海沟沉积一般比深海盆地堆积速度更快, 堆积厚度也更大, 但在海沟的不同位置或不同海沟之间, 堆积厚度也会有所不同。海沟的这些沉积机理和沉积过程的差异, 影响了海沟沉积物的性质, 包括沉积物粒度、矿物、生物等都有所差异。文章根据海沟以上的沉积特点, 分析了不同海沟之间和同一海沟内部海沟沉积厚度以及沉积物的粒度特征、矿物组成和生物特征的差异, 并总结了海沟重力滑塌、浊流沉积、火山活动、生物化学沉积、漏斗效应这五种海沟沉积机理对海沟沉积物沉积过程的影响。文章最后展望了海沟沉积物的研究热点, 希望在此基础上促进海沟沉积物的进一步研究。
中图分类号:
- P736.2
引用本文
肖春晖, 王永红, 林间. 海沟沉积物研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(6): 27-38.
Chunhui XIAO, Yonghong WANG, Jian LIN. Research progress on ocean trench sedimentation[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2017, 36(6): 27-38.
| [1] | 本座荣一, 1985. 印度洋、太平洋板块边界区域中岛弧、海沟系地质构造研究成果简报[J]. 白桦, 译. 地质科技情报, (3): 38. |
| [2] | #cod#x00412;#cod#x0041b;#cod#x00410;#cod#x00421;#cod#x0041e;#cod#x00412; #cod#x00413; #cod#x0041c;, 1995. 太平洋深海钻探和板块构造总结[J]. 朱佛宏, 译. 海洋地质动态, (7): 11-13. |
| [3] | 陈志豪, 吴能友, 李家彪, 2010. 马尼拉海沟俯冲带增生楔中天然气水合物的流体运移通道[J]. 现代地质, 24(3): 441-449 |
| CHEN ZHIHAO, WU NENGYOU, LI JIABIAO, 2010. Pathway of fluid migration for gas hydrate in the accretionary wedge of Manila Subduction Zone, Northeastern South China Sea[J]. Geoscience, 24(3): 441-449 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 成国栋, 李永植, 1979. IPOD计划在日本海沟钻探工作的初步成果简介[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, (2): 121-128. |
| [5] | 冯俊熙, 罗敏, 胡钰, 等, 2016. 海底蛇纹岩化伴生的碳酸盐岩研究进展[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报, 35(4): 789-799 |
| FENG JUNXI, LUO MIN, HU YU, et al, 2016. Progress of the research on authigenic carbonates associated with oceanic serpentinization[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry, 35(4): 789-799 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | #cod#x0041a;#cod#x00418;#cod#x00420;#cod#x00418;#cod#x0041b;#cod#x0041b;#cod#x0041e;#cod#x0042a; #cod#x00393; #cod#x0041b;, 1992. 菲律宾海深海沟的构造与演化[J]. 舒欣, 译. 海洋石油, 12(3): 32-39. |
| [7] | 李家彪, 金翔龙, 阮爱国, 等, 2004. 马尼拉海沟增生楔中段的挤入构造[J]. 科学通报, 49(10): 1000-1008. |
| [8] | 林长松, 王冠荣, 1992. 马里亚纳岛弧系的垂向旋转运动与海槽的形成[J]. 海洋学报, 14(5): 86-94. |
| [9] | 林美华, 李乃胜, 1998. 琉球海沟构造地貌[J]. 青岛海洋大学学报, 28(3): 497-502 |
| LIN MEIHUA, LI NAISHENG, 1998. On the structural landforms of the Ryukyu Trench[J]. Journal of Ocean University of QingDao, 28(3): 497-502 (in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 卢效珍, 1992. 太平洋中部柱状沉积物中的自生矿物[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 12(1): 67-72 |
| LU XIAOZHEN, 1992. Authigenic minerals in a sediment column from the central pacific[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 12(1): 67-72 (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | OKADA H, 张旺生, 1989. 海沟面貌[J]. 宝石和宝石学杂志, (2): 40-42. |
| [12] | 彭汉昌, 刘正坤, 1992. 深海沉积物中的钙十字沸石[J]. 海洋学报, 14(6): 68-73. |
| [13] | .任建业, 2008. 海洋底构造导论[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社 133-156 |
| REN JIANYE, 2008. An introduction to ocean floor tectonics[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press: 133-156 (in Chinese). | |
| [14] | 宋永东, 马小川, 张广旭, 等, 2016. 西太平洋雅浦海沟区海底热流原位测量[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(4): 51-56 |
| SONG YONGDONG, MA XIAOCHUAN, ZHANG GUANGXU, et al, 2016. Heat flow in-situ measurement at yap trench of the western pacific[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 36(4): 51-56 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | 王汾连, 何高文, 王海峰, 等, 2016. 马里亚纳海沟柱状沉积物稀土地球化学特征及其指示意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(4): 67-75 |
| WANG FENLIAN, HE GAOWEN, WANG HAIFENG, et al, 2016. Geochemistry of rare earth elements in a core from Mariana Trench and its significance[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 36(4): 67-75 (in Chinese). | |
| [16] | 王海峰, 朱克超, 邓希光, 2015. 马里亚纳海沟JL7KBC03短柱沉积地质特征[J]. 地质论评, 61(S): 914-915. |
| [17] | 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 等, 2008a. 南海北部陆坡的地貌形态及其控制因素[J]. 海洋学报, 30(2): 70-79 |
| WANG HAIRONG, WANG YINGMIN, QIU YAN, et al, 2008a. Geomorphology and its control of deep-water slope of the margin of the South China Sea[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 30(2): 70-79 (in Chinese). | |
| [18] | 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 2008b. 南海东北部台湾浅滩陆坡的浊流沉积物波的发育及其成因的构造控制[J]. 沉积学报, 26(1): 39-45 |
| WANG HAIRONG, WANG YINGMIN, QIU YAN, 2008b. Development and its tectonic activity#cod#x02019;s origin of turbidity current sediment wave in Manila Trench, the South China Sea[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica, 26(1): 39-45 (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 王海荣, 王英民, 邱燕, 等, 2009. 深水环境多级地貌坡折控制下的重力流动力学的演变[J]. 地质学报, 83(6): 812-819 |
| WANG HAIRONG, WANG YINGMIN, QIU YAN, et al, 2009. The control of the multiple geomorphologic breaks on evolution of gravity flow dynamics in deep-water environment[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 83(6): 812-819 (in Chinese). | |
| [20] | 汪品先, 2009. 深海沉积与地球系统[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 29(4): 1-10 |
| WANG PINXIAN, 2009. Deep sea sediments and Earth system[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 29(4): 1-10 (in Chinese). | |
| [21] | .王琦, 朱而勤, 1989. 海洋沉积学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社: 1-253. |
| [22] | 肖荣阁, 刘敬党, 费红彩, 等, 2015. 沉积相稀土地球化学标志[J]. 地球科学前沿, 5(3): 193-234 |
| XIAO RONGGE, LIU JINGDANG, FEI HONGCAI, et al, 2015. REE geochemical characteristics of sedimentary facies[J]. Advances in Geosciences, 5(3): 193-234 (in Chinese). | |
| [23] | 肖益林, 孙贺, 顾海欧, 等, 2015. 大陆深俯冲过程中的熔流体成分与地球化学分异[J]. 中国科学: 地球科学, 58(9): 1457-1476 |
| XIAO YILIN, SUN HE, GU HAIOU, et al, 2015. Fluid/melt in continental deep subduction zones: Compositions and related geochemical fractionations[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 58(9): 1457-1476 (in Chinese). | |
| [24] | 熊衎昕, 俞何興, 2012. 以從源到匯之觀點探討臺灣西南外海沈積物散佈系統及傳輸之意義[J]. 鑛冶, (220): 7-15 |
| HSIUNG K H, YU H S, 2012. Sediment dispersal system and transport from mountain source to oceanic sink off Southwestern Taiwan[J]. Mining and Metallurgical, (220): 7-15 (in Chinese). | |
| [25] | 熊志方, 李铁刚, 翟滨, 等, 2010. 低纬度西太平洋末次冰期Ethmodiscus rex硅藻席黏土矿物特征及形成机制启示[J]. 地球科学#cod#x02014;中国地质大学学报, 35(4): 551-562 |
| XIONG ZHIFANG, LI TIEGANG, ZHAI BIN, et al, 2010. Clay mineral characteristics of Ethmodiscus rex diatom mats from low-latitude Western Pacific during the last glacial and implications for their formation[J]. Earth Science#cod#x02014;Journal of China University of Geosciences, 35(4): 551-562 (in Chinese). | |
| [26] | 徐兆凯, 李安春, 蒋富清, 等, 2008. 东菲律宾海沉积物的地球化学特征与物质来源[J]. 科学通报, 53(6): 695-702. |
| [27] | .喻普之, 李乃胜, 1992. 东海地壳热流[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 1-127. |
| [28] | 张斌, 李广雪, 黄继峰, 2014. 菲律宾海构造地貌特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 34(2): 79-88 |
| ZHANG BIN, LI GUANGXUE, HUANG JIFENG, 2014. The tectonic geomorphology of the Philippine Sea[J]. Marine Geology #cod#x00026; Quaternary Geology, 34(2): 79-88 (in Chinese). | |
| [29] | .张富元, 章伟艳, 张霄宇, 等, 2013. 深海沉积物分类与命名[M]. 北京: 海洋出版社: 39-44. |
| [30] | 张金鹏, 邓希光, 杨胜雄, 等, 2015. 马里亚纳海沟挑战者深渊南部7000m水深处发现硅藻化石软泥[J]. 地质通报, 34(12): 2352-2354 |
| ZHANG JINPENG, DENG XIGUANG, YANG SHENGXIONG, et al, 2015. Diatom ooze found in 7000m submarine area of challenger depth in Mariana trench[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 34(12): 2352-2354 (in Chinese). | |
| [31] | 张金鹏, 邓希光, 朱本铎, 等, 2016. 西太平洋挑战者深渊海底浅表层的硅藻软泥[J]. 微体古生物学报, 33(1): 1-8 |
| ZHANG JINPENG, DENG XIGUANG, ZHU BENDUO, et al, 2016. Diatom ooze from the surface sediments in the challenger deep of the Western Pacific Ocean[J]. Acta Micropalaeontologica Sinica, 33(1): 1-8 (in Chinese). | |
| [32] | 朱俊江, 丘学林, 詹文欢, 等, 2005. 南海东部海沟的震源机制解及其构造意义[J]. 地震学报, 27(3): 260-268 |
| ZHU JUNJIANG, QIU XUELIN, ZHAN WENHUAN, et al, 2005. Focal mechanism solutions and its tectonic significance in the trench of the Eastern South China Sea[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27(3): 260-268 (in Chinese). | |
| [33] | 朱坤杰, 何树平, 陈芳, 等, 2015. 马里亚纳海沟南部海域沉积物的工程地质特性及其成因[J]. 地质学刊, 39(2): 251-257 |
| ZHU KUNJIE, HE SHUPING, CHEN FANG, et al, 2015. Engineering geological characteristics and genesis of the sediments from the Southern Mariana Trench[J]. Journal of Geology, 39(2): 251-257 (in Chinese). | |
| [34] | AKIMOTO K, HATTORI M, UEMATSU K, et al, 2001. The deepest living foraminifera, Challenger Deep, Mariana Trench[J]. Marine Micropaleontology, 42(1-2): 95-97. |
| [35] | ANIKOUCHINE W A, LING H Y, 1967. Evidence for turbidite accumulation in trenches in the Indo-Pacific region[J]. Marine Geology, 5(2): 141-154. |
| [36] | BANDY O L, RODOLFO K S, 1964. Distribution of foraminifera and sediments, Peru-Chile Trench area[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 11(5): 817-837. |
| [37] | BECKER J J, SANDWELL D T, SMITH W H F, et al, 2009. Global bathymetry and elevation data at 30 arc seconds resolution: SRTM30_PLUS[J]. Marine Geodesy, 32(4): 355-371. |
| [38] | BLUMBERG S, LAMY F, ARZ H W, et al, 2008. Turbiditic trench deposits at the South-Chilean active margin: a Pleistocene-Holocene record of climate and tectonics[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 268(3-4): 526-539. |
| [39] | BOURGET J, ZARAGOSI S, ELLOUZ-ZIMMEERMANN N, et al, 2011. Turbidite system architecture and sedimentary processes along topographically complex slopes: the Makran convergent margin[J]. Sedimentology, 58(2): 376-406. |
| [40] | BOWIN C O, NALWALK A J, HERSEY J B, 1966. Serpentinized peridotite from the north wall of the Puerto Rico trench[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 77(3): 257-270. |
| [41] | CHANDRALATA RAGHUKUMAR, SESHAGIRI RAGHUKUMAR, SHEELU G, et al.2004.Buried in time: culturable fungi in a deep-sea sediment core from the Chagos Trench, Indian Ocean[J]. Deep-Sea Research I 51(11): 1759-1768. |
| [42] | CHASE R L, HERSEY J B, 1968. Geology of the north slope of the Puerto Rico Trench[J]. Deep-Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 15(3): 297-317. |
| [43] | CONOLLY J R, EWING M W, 1967. Sedimentation in the puerto rico trench[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 37(1): 44-59. |
| [44] | CONTRERAS-REYES E, JARA J, MAKSYMOWICZ A, et al, 2013. Sediment loading at the Southern Chilean trench and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 66: 134-145. |
| [45] | CURTIS A C, WAHEAT C G, FRYER P, et al, 2005. Mariana forearc serpentinite mud volcanoes harbor novel communities of extremophilic Archaea[J]. Geomicrobiology Journal, 30(5): 430-441. |
| [46] | DANOVARO R, GAMBI C, CROCE N D, et al, 2002. Meiofauna hotspot in the Atacama Trench, eastern South Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 49(5): 843-857. |
| [47] | DENG XIGUANG, YI LIANG, PATERSON G A, et al, 2016. Magnetostratigraphic evidence for deep-sea erosion on the Pacific Plate, south of Mariana Trench, since the middle Pleistocene: potential constraints for Antarctic bottom water circulation[J]. International Geology Review, 58(1): 49-57. |
| [48] | DUNCAN M S, DASGUPTA R, 2014. CO2 solubility and speciation in rhyolitic sediment partial melts at 1.5~3.0 GPa-Implications for carbon flux in subduction zones[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 124: 328-347. |
| [49] | EPPING E, 2013. Ocean ecology: life in an oceanic extreme[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(4): 252-253. |
| [50] | FANG JIASONG, BARCELONA M J, NOGI Y, et al, 2000. Biochemical implications and geochemical significance of novel phospholipids of the extremely barophilic bacteria from the Marianas Trench at 11,000 m[J]. Deep sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 47(6): 1173-1182. |
| [51] | FREZZOTTI M L, HUIZENGA J M, COMPAGNONI R, et al, 2014. Diamond formation by carbon saturation in C-O-H fluids during cold subduction of oceanic lithosphere[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 68-86. |
| [52] | FRYER P, 2012. Serpentinite mud volcanism: Observations, processes, and implications[J]. Annual Review of Marine Science, 4: 345-373. |
| [53] | GARDNER J V, ARMSTRONG A A, CALDER B R, et al, 2014. So, how deep is the Mariana Trench?[J]. Marine Geodesy, 37(1): 1-13. |
| [54] | GLUD R N, WENZH#cod#x000d6;FER F, MIDDELBOE M, et al, 2013. High rates of microbial carbon turnover in sediments in the deepest oceanic trench on Earth[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(4): 284-288. |
| [55] | HANYU T, KAWABATA H, TATSUMI Y, et al, 2014. Isotope evolution in the HIMU reservoir beneath St. Helena: Implications for the mantle recycling of U and Th[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 232-252. |
| [56] | HEBERER B, ROSER G, BEHRMANN J H, et al, 2010. Holocene sediments from the Southern Chile Trench: a record of active margin magmatism, tectonics and palaeoseismicity[J]. Journal of the Geological Society, 167(3): 539-553. |
| [57] | HEEZEN B C, NAFE J E, 1964. Vema trench: western Indian ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 11(1): 79-84. |
| [58] | HEEZEN B C, JOHNSON G L, 1965. The South Sandwich Trench[J]. Deep Sea Research and Oceanographic Abstracts, 12(2): 185-197. |
| [59] | HEURET A, CONRAD C P, FUNICIELLO F, et al, 2012. Relation between subduction megathrust earthquakes, trench sediment thickness and upper plate strain[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 39(5): L05304. |
| [60] | .HOPKIN M, (2005-02-03) [2016-12-13]. Muddy microbes retrieved from the abyss[EB/OL]. . |
| [61] | HUSSONG D M, UYEDA S, 1982. Tectonic processes and the history of the Mariana Arc: a synthesis of the results of deep sea drilling project leg 60[J]. Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, 60: 909-929. |
| [62] | ICHINO M C, CLARK M R, DRAZEN J C, et al, 2015. The distribution of benthic biomass in hadal trenches: A modelling approach to investigate the effect of vertical and lateral organic matter transport to the seafloor[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 100: 21-33. |
| [63] | ITOH M, KAWAMURA K, KITAHASHI T, et al, 2011. Bathymetric patterns of meiofaunal abundance and biomass associated with the Kuril and Ryukyu trenches, western North Pacific Ocean[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 58(1): 86-97. |
| [64] | KHARLAMENKO V I, W#cod#x000dc;RZBERG L, PETERS J, et al, 2015. Fatty acid compositions and trophic relationships of shelled molluscs from the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench and the adjacent abyssal plain[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 111: 389-398. |
| [65] | KITAHASHI T, KAWAMURA K, KOJIMA S, et al, 2013. Assemblages gradually change from bathyal to hadal depth: A case study on harpacticoid copepods around the Kuril Trench (north-west Pacific Ocean)[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 74: 39-47. |
| [66] | KITAHASHI T, KAWAMURA K, KOJIMA S, et al, 2014. Bathymetric patterns of #cod#x003b1; and #cod#x003b2; diversity of harpacticoid copepods at the genus level around the Ryukyu Trench, and turnover diversity between trenches around Japan[J]. Progress in Oceanography, 123: 54-63. |
| [67] | KUKOWSKI N, SCHILLHORN T, HUHN K, et al, 2001. Morphotectonics and mechanics of the central Makran accretionary wedge off Pakistan[J]. Marine Geology, 173(1-4): 1-19. |
| [68] | LEDUC D, ROWDEN A A, GLUD R N, et al, 2016. Comparison between infaunal communities of the deep floor and edge of the Tonga Trench: possible effects of differences in organic matter supply[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 116: 264-275. |
| [69] | LUO MIN, GIESKES J, CHEN LINYING, et al, 2017. Provenances, distribution, and accumulation of organic matter in the southern Mariana Trench rim and slope: Implication for carbon cycle and burial in hadal trenches[J]. Marine Geology, 386: 98-106, doi: 10.1016/ j.margeo.2017.02.012. |
| [70] | MALLIK T K, 1976. Shelf sediments of the Ganges delta with special emphasis on the mineralogy of the western part, Bay of Bengal, Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 22(1): 1-32. |
| [71] | MALLIK T K, 1978. Mineralogy of deep-sea sands of the Indian Ocean[J]. Marine Geology, 27(1-2): 161-176. |
| [72] | MIKHAIL S, DOBOSI G, VERCHOVSKY A B, et al, 2013. Peridotitic and websteritic diamondites provide new information regarding mantle melting and metasomatism induced through the subduction of crustal volatiles[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 107: 1-11. |
| [73] | MONECKE K, FINGER W, KLARER D, et al, 2008. A 1,000-year sediment record of tsunami recurrence in northern Sumatra[J]. Nature, 455(7217): 1232-1234. |
| [74] | MORRILL P L, KUENEN J G, JOHNSON Q J, et al, 2013. Geochemistry and geobiology of a present-day serpentinization site in california: the cedars[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 109: 222-240. |
| [75] | MULDER T, H#cod#x000dc;NEKE H, VAN LOON A J, 2011. Progress in deep-sea sedimentology[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 63: 1-24. |
| [76] | .NUNOURA T, TAKAKI Y, HIRAI M, et al, 2015. Hadal biosphere: Insight into the microbial ecosystem in the deepest ocean on Earth[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 112(11): E1230-E1236. |
| [77] | REA D K, RUFF L J, 1996. Composition and mass flux of sediment entering the world#cod#x02019;s subduction zones: Implications for global sediment budgets, great earthquakes, and volcanism[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 140(1-4): 1-12. |
| [78] | RUFF L J, 1989. Do Trench sediments affect great earthquake occurrence in subduction zones?[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 129(1-2): 263-282. |
| [79] | SABBATINI A, MORIGI C, NEGRI A, et al, 2002. Soft-shelled benthic foraminifera from a hadal site (7800 m water depth) in the Atacama Trench (SE Pacific): preliminary observations[J]. Journal of Micropalaeontology, 21(2): 131-135. |
| [80] | SATTAROVA V V, ARTEMOVA A V, 2015. Geochemical and micropaleontological character of Deep-Sea sediments from the Northwestern Pacific near the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 111: 10-18. |
| [81] | SCHL#cod#x000dc;TER H U, PREXL A, GAEDICKE C, et al, 2002. The Makran accretionary wedge: sediment thicknesses and ages and the origin of mud volcanoes[J]. Marine Geology, 185(3-4): 219-232. |
| [82] | SCHMIDT C, ARBIZU P M, 2015. Unexpectedly higher metazoan meiofauna abundances in the Kuril-Kamchatka Trench compared to the adjacent abyssal plains[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 111: 60-75. |
| [83] | SCHOLL D W, 1974. Sedimentary sequences in the North Pacific trenches[M]//BURK C A, DRAKE C L. The Geology of Continental Margins. New York: Springer-Verlag: 493-504. |
| [84] | SMITH G L, MCNEILLL C, WANG KELIN, et al, 2013. Thermal structure and megathrust seismogenic potential of the Makran subduction zone[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 40(8): 1528-1533. |
| [85] | TATSUMI Y, SUZUKI T, OZAWA H, et al, 2014. Accumulation of #cod#x02018;anti-continent#cod#x02019; at the base of the mantle and its recycling in mantle plumes[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 23-33. |
| [86] | VANHOVE S, VERMEEREN H, VANREUSEL A, 2004. Meiofauna towards the South Sandwich Trench (750-6300 m), focus on nematodes[J]. Deep Sea Research Part II: Topical Studies in Oceanography, 51(14-16): 1665-1687. |
| [87] | VON HUENE R, LANGSETH M, NASU N, et al, 1982. A summary of cenozoic tectonic history along the IPOD Japan Trench transect[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 93(9): 829-846. |
| [88] | VON HUENE R, CULOTTA R, 1989. Tectonic erosion at the front of the Japan Trench convergent margin[J]. Tectonophysics, 160(1-4): 75-90. |
| [89] | WENZH#cod#x000d6;FER F, OGURI K, MIDDELBOE M, et al, 2016. Benthic carbon mineralization in hadal trenches: assessment by in situ O2 microprofile measurements[J]. Deep Sea Research Part I: Oceanographic Research Papers, 116: 276-286. |
| [90] | XU YIGANG, 2014. Recycled oceanic crust in the source of 90-40 Ma basalts in North and Northeast China: Evidence, provenance and significance[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 49-67. |
| [91] | XU ZHENG, ZHENG YONGFEI, ZHAO ZIFU, et al, 2014. The hydrous properties of subcontinental lithospheric mantle: Constraints from water content and hydrogen isotope composition of phenocrysts from Cenozoic continental basalt in North China[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 285-302. |
| [92] | YANG WUBIN, NIU HECAI, SHAN QIANG, et al, 2014. Geochemistry of primary-carbonate bearing K-rich igneous rocks in the Awulale Mountains, western Tianshan: implications for carbon-recycling in subduction zone[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 143: 143-164. |
| [93] | ZHANG FAN, LIN JIAN, ZHAN WENHUAN, 2014. Variations in oceanic plate bending along the Mariana Trench[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 401: 206-214. |
| [94] | ZHOU ZHIYUAN, LIN JIAN, BEHN M D, et al, 2015. Mechanism for normal faulting in the subducting plate at the Mariana Trench[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42(11): 4309-4317. |
| [1] | 莫丹杨, 宁志铭, 杨斌, 夏荣林, 刘志金. 涠洲岛珊瑚礁区沉积物硝酸盐异化还原过程对温度变化的响应[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(4): 137-143. |
| [2] | 高洁, 余克服, 许慎栋, 黄学勇, 陈飚, 王永刚. 西沙群岛永乐环礁礁外坡沉积物中有机碳的含量与来源分析[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2024, 43(3): 131-145. |
| [3] | 邢楠楠, 任润馨, 唐振洲, 罗志宏, 夏辰曦, 刘永宏, 彭亮, 陈显强. 涠洲岛海洋沉积物来源真菌Aspergillus sp. GXIMD02003的代谢产物研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 154-160. |
| [4] | 孙翠慈, 岳维忠, 赵文杰, 王友绍. 大亚湾表层沉积物碳水化合物活性酶基因分布特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2023, 42(5): 76-91. |
| [5] | 李震, 李云凯, 刘永虎, 程前, 张硕. 渤海表层沉积物中化学浸取不同形态氮的释放潜力[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 163-171. |
| [6] | 王朝晖, 张宇宁, 王文婷, 谢昌良, 陈佳卓, 郑虎, 王军星. 福建东山湾表层沉积物中甲藻孢囊分布研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(4): 154-162. |
| [7] | 李华薇, 徐向荣. 中国典型红树林沉积物中多溴联苯醚和替代型溴系阻燃剂污染特征[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2022, 41(1): 117-130. |
| [8] | 倪玉根, 李建国, 习龙. 海砂粒级划分标准和沉积物命名方法探讨*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(3): 143-151. |
| [9] | 戴晓娟, 胡韧, 罗洪添, 王庆, 胡晓娟, 白敏冬, 杨宇峰. 大型海藻龙须菜凋落物分解对水质的影响[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2021, 40(1): 91-98. |
| [10] | 张杰, 李琦. 东海南部内陆架泥质区S05-2孔沉积物4870a BP以来的沉积学记录及其对物源与季风演化指示*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2020, 39(5): 84-97. |
| [11] | 朱士兵,胡丹妮,张会领,曾春华,李泽华,李志强. 海口湾中间岸段海滩剖面短期时空变化及沉积动态分析 *[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(5): 77-85. |
| [12] | 来志庆, 刘海青, 林霖, 韩宗珠, 国坤. 单颗粒碎屑矿物在海洋沉积物物源分析中的应用*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2019, 38(1): 85-95. |
| [13] | 罗云, 侯正瑜, 田雨杭, 许安涛, 陈忠. 南海海底沉积物声学物理参数测定的温度和时间优化研究[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2018, 37(4): 81-88. |
| [14] | 杜恕环, 向荣, 陈木宏, 刘建国, 张兰兰, 罗传秀, 苏翔, 张强. 印度洋沉积物中火山灰应用研究进展[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(6): 12-18. |
| [15] | 刘涛, 刘莹, 乐远福. 红树林湿地沉积速率对于气候变化的响应*[J]. 热带海洋学报, 2017, 36(2): 40-47. |
|
||